Detection of renal cell carcinoma using plasma and urine cell-free DNA methylomes
- PMID: 32572266
- PMCID: PMC8288043
- DOI: 10.1038/s41591-020-0933-1
Detection of renal cell carcinoma using plasma and urine cell-free DNA methylomes
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Detection of renal cell carcinoma using plasma and urine cell-free DNA methylomes.Nat Med. 2020 Oct;26(10):1663. doi: 10.1038/s41591-020-1078-y. Nat Med. 2020. PMID: 32895574
Abstract
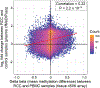
Improving early cancer detection has the potential to substantially reduce cancer-related mortality. Cell-free methylated DNA immunoprecipitation and high-throughput sequencing (cfMeDIP-seq) is a highly sensitive assay capable of detecting early-stage tumors. We report accurate classification of patients across all stages of renal cell carcinoma (RCC) in plasma (area under the receiver operating characteristic (AUROC) curve of 0.99) and demonstrate the validity of this assay to identify patients with RCC using urine cell-free DNA (cfDNA; AUROC of 0.86).
Figures



Comment in
-
Blood Test Catches Cancers That Shed Little DNA.Cancer Discov. 2020 Sep;10(9):1246-1247. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-NB2020-068. Epub 2020 Jul 14. Cancer Discov. 2020. PMID: 32665301
-
Closing in on cfDNA-based detection and diagnosis.Nat Rev Cancer. 2020 Sep;20(9):481. doi: 10.1038/s41568-020-0293-7. Nat Rev Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32690930 No abstract available.
-
Methylation extends the reach of liquid biopsy in cancer detection.Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2020 Nov;17(11):655-656. doi: 10.1038/s41571-020-0420-0. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32732909 Free PMC article.
-
cfDNA methylation analysis detects RCC.Nat Rev Urol. 2020 Oct;17(10):543. doi: 10.1038/s41585-020-0366-0. Nat Rev Urol. 2020. PMID: 32782365 No abstract available.
References
-
- Shen SY et al. Sensitive tumour detection and classification using plasma cell-free DNA methylomes. Nature 563, 579–583 (2018). - PubMed
-
- Shen SY Burgener JM Bratman SV & De Carvalho DD Preparation of cfMeDIP-seq libraries for methylome profiling of plasma cell-free DNA. Nat. Protoc. 14, 2749–2780 (2019). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

