The role of initial chest X-ray in triaging patients with suspected COVID-19 during the pandemic
- PMID: 32572707
- PMCID: PMC7306559
- DOI: 10.1007/s10140-020-01808-y
The role of initial chest X-ray in triaging patients with suspected COVID-19 during the pandemic
Abstract
Purpose: The purpose of our research is to evaluate the usefulness of chest X-ray for triaging patients with suspected COVID-19 infection.
Methods: IRB approval was obtained to allow a retrospective review of adult patients who presented to the Emergency Department with a complaint of fever, cough, dyspnea or hypoxia and had a chest X-ray between 12 March 2020 and 26 March 2020. The initial chest X-ray was graded on a scale of 0-3 with grade 0 representing no alveolar opacities, grade 1: < 1/3 alveolar opacities of the lung, Grade 2: 1/3 to 2/3 lung with alveolar opacities and grade 3: > 2/3 alveolar opacities of the lung. Past medical history of diabetes and hypertension, initial oxygen saturation, COVID-19 testing results, intubation, and outcome were also collected.
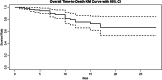
Results: Four hundred ten patient chest X-rays were reviewed. Oxygen saturation and X-ray grade were both significantly associated with the length of stay in hospital, the hazard ratio (HR) of discharge was 1.05 (95% CI [1.01, 1.09], p = 0.017) and 0.61 (95% CI [0.51, 0.73], p < 0.001), respectively. In addition, oxygen saturation and X-ray grade were significant predictors of intubation (odds ratio (OR) of intubation is 0.88 (95% CI [0.81, 0.96], p = 0.004) and 3.69 (95% CI [2.25, 6.07], p < 0.001).
Conclusions: Initial chest X-ray is a useful tool for triaging those subjects who might have poor outcomes with suspected COVID-19 infection and benefit most from hospitalization.
Keywords: COVID-19; CXR; Chest; Coronavirus; SARS-CoV-2; X-ray.
Conflict of interest statement
Mary Salvatore, MD is a speaker and consultant for Genentech and Boehringer Ingelheim, and received grant funding from Genentech, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Lunglife AI.
Figures

References
-
- Li Q, Guan X, Wu P, Wang X, Zhou L, Tong Y, Ren R, Leung KSM, Lau EHY, Wong JY, Xing X, Xiang N, Wu Y, Li C, Chen Q, Li D, Liu T, Zhao J, Liu M, Tu W, Chen C, Jin L, Yang R, Wang Q, Zhou S, Wang R, Liu H, Luo Y, Liu Y, Shao G, Li H, Tao Z, Yang Y, Deng Z, Liu B, Ma Z, Zhang Y, Shi G, Lam TTY, Wu JT, Gao GF, Cowling BJ, Yang B, Leung GM, Feng Z. Early transmission dynamics in Wuhan, China, of novel coronavirus-infected pneumonia. N Engl J Med. 2020;382:1199–1207. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa2001316. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alonso-Zaldivar R. With Worst Expected to Come, 3 out of 4 U.S. Hospitals Are Treating Patients with COVID-19. Fortune. Published on line April 6, 2020
-
- Hadaya J, Schumm M, Livingston EH (2020) Testing individuals for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19). JAMA - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

