Lidocaine spray versus viscous lidocaine solution for pharyngeal local anesthesia in upper gastrointestinal endoscopy: Systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 32573016
- PMCID: PMC12136277
- DOI: 10.1111/den.13775
Lidocaine spray versus viscous lidocaine solution for pharyngeal local anesthesia in upper gastrointestinal endoscopy: Systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Objectives: There are two major methods for local anesthesia by lidocaine before upper gastrointestinal endoscopy: simple spray and viscous solution. We aimed to assess the efficacy and safety by meta-analysis between these two methods.
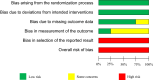
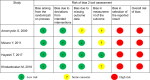
Methods: We searched PubMed, EMBASE, the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials, World Health Organization International Clinical Trials Registry Platform, and ClinicalTrials.gov databases through October 2019 to perform meta-analyses using random-effects models. The primary outcomes were participants' pain/discomfort, satisfaction, and anaphylactic shock. Three reviewers independently searched for articles, extracted data, and assessed the risk of bias. We evaluated the certainty of evidence based on the Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development, and Evaluation approach. This study was registered in PROSPERO (CRD42020155611).
Results: We included seven randomized controlled trials (2667 participants). The participants' pain/discomfort may be similar between the lidocaine spray and viscous solution [standardized mean difference 0.03, 95% confidence intervals (CI) -0.37 to 0.42; I2 = 93%; low certainty of evidence]. The lidocaine spray probably increased participants' satisfaction compared with the viscous solution (relative risk 1.22; 95% CI, 1.02 to 1.47; I2 = 47%; moderate certainty of evidence). No anaphylactic shock occurred in four studies (low certainty of evidence). Four studies had high risks of selection bias.
Conclusion: The use of lidocaine spray for local anesthesia provided better satisfaction scores than the viscous solution, and both methods have the same effect with regards to the control of discomfort and pain. Further studies in large multicenter randomized controlled trials with a pre-registration protocol are needed.
Keywords: endoscopy; lidocaine; oral sprays; systematic review; viscosity.
© 2020 Japan Gastroenterological Endoscopy Society.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare no conflicts of interest for this article.
Figures


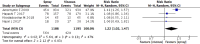

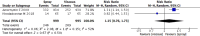
References
-
- Pimentel‐Nunes P, Libânio D, Marcos‐Pinto R et al. Management of epithelial precancerous conditions and lesions in the stomach (MAPS II): European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE), European Helicobacter and Microbiota Study Group (EHMSG), European Society of Pathology (ESP), and Sociedade Portuguesa de Endoscopia Digestiva (SPED) guideline update 2019. Endoscopy 2019; 51: 365–88. - PubMed
-
- Zhang X, Li M, Chen S et al. Endoscopic screening in Asian countries is associated with reduced gastric cancer mortality: A meta‐analysis and systematic review. Gastroenterology 2018; 155: 347–54. - PubMed
-
- Campo R, Brullet E, Montserrat A et al. Identification of factors that influence tolerance of upper gastrointestinal endoscopy. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 1999; 11: 201–4. - PubMed
-
- Brandt LJ. Patients' attitudes and apprehensions about endoscopy: How to calm troubled waters. Am J Gastroenterol 2001; 96: 280–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

