Epidemiological and Clinical Characteristics of Patients With Coronavirus Disease-2019 in Shiyan City, China
- PMID: 32574282
- PMCID: PMC7256435
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00284
Epidemiological and Clinical Characteristics of Patients With Coronavirus Disease-2019 in Shiyan City, China
Abstract
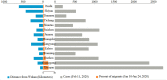
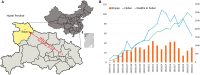
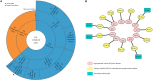
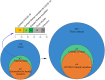
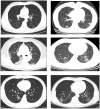
To investigate the early epidemic of COVID-19, a total of 176 confirmed COVID-19 cases in Shiyan city, Hubei province, China were surveyed. Our data indicated that the rate of emergence of early confirmed COVID-19 cases in Hubei province outside Wuhan was dependent on migration population, and the second-generation of patients were family clusters originating from Wuhan travelers. Epidemiological investigation indicated that the reproductive number (R0) under containment strategies was 1.81, and asymptomatic SARS-CoV-2 carriers were contagious with a transmission rate of 10.7%. Among the 176 patients, 53 were admitted to the Renmin Hospital of Hubei University of Medicine. The clinical characteristics of these 53 patients were collected and compared based on a positive RT-PCR test and presence of pneumonia. Clinical data showed that 47.2% (25/53) of COVID-19 patients were co-infected with Mycoplasma pneumoniae, and COVID-19 patients coinfected with M. pneumoniae had a higher percentage of monocytes (P < 0.0044) and a lower neutrophils percentage (P < 0.0264). Therefore, it is important to assess the transmissibility of infected asymptomatic individuals for SARS-CoV-2 transmission; moreover, clinicians should be alert to the high incidence of co-infection with M. pneumoniae in COVID-19 patients.
Keywords: COVID-19; Mycoplasma pneumonia; SARS-CoV-2; asymptomatic infections; coinfection.
Copyright © 2020 Liu, Lei, Xiao, Yang, Li, Ji, Du, Tan, Zhu, Li, Jin, Liu, Wu and Liu.
Figures
References
-
- Chan J. F., Yip C. C., To K. K., Tang T. H., Wong S. C., Leung K. H., et al. . (2020a). Improved molecular diagnosis of COVID-19 by the novel, highly sensitive and specific COVID-19-RdRp/Hel real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction assay validated in vitro and with clinical specimens. J. Clin. Microbiol. 58:e00310-20. 10.1128/JCM.00310-20 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen H. J., Guo J. J., Wang C., Luo F., Yu X., Zhang P. W., et al. . (2020). Clinical characteristics and intrauterine vertical transmission potential of COVID-19 infection in nine pregnant women: a retrospective review of medical records. Lancet 395, 809–815. 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30360-3 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

