Economic Consequences of the COVID-19 Outbreak: the Need for Epidemic Preparedness
- PMID: 32574307
- PMCID: PMC7273352
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2020.00241
Economic Consequences of the COVID-19 Outbreak: the Need for Epidemic Preparedness
Abstract
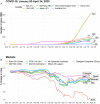
COVID-19 is not only a global pandemic and public health crisis; it has also severely affected the global economy and financial markets. Significant reductions in income, a rise in unemployment, and disruptions in the transportation, service, and manufacturing industries are among the consequences of the disease mitigation measures that have been implemented in many countries. It has become clear that most governments in the world underestimated the risks of rapid COVID-19 spread and were mostly reactive in their crisis response. As disease outbreaks are not likely to disappear in the near future, proactive international actions are required to not only save lives but also protect economic prosperity.
Keywords: COVID-19; Coronavirus; SARS-CoV-2; economy; global markets; pandemic.
Copyright © 2020 Pak, Adegboye, Adekunle, Rahman, McBryde and Eisen.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): Situation Report 100. Geneva: (2020).
-
- Global Preparedness Monitoring Board A world at Risk: Annual Report on Global Preparedness for Health Emergencies. Geneva: World Health Organization; (2019).
-
- Katz R, Wentworth M, Quick J, Arabasadi A, Harris E, Geddes K, et al. Enhancing public–private cooperation in epidemic preparedness and response. World Med Health Policy. (2018) 10:420–5. 10.1002/wmh3.281 - DOI
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

