Clinical Presentation and Outcomes of Pregnant Women With Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
- PMID: 32575114
- PMCID: PMC7337697
- DOI: 10.1093/cid/ciaa828
Clinical Presentation and Outcomes of Pregnant Women With Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Descriptions of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) have focused on the nonpregnant adult population. This study aims to describe the clinical characteristics and perinatal outcomes of COVID-19 in pregnancy.
Methods: We searched databases from December 2019 to 30 April 2020. Eligible studies reported clinical characteristics, radiological findings, and/or laboratory testing of pregnant women during infection. Data were pooled across studies using a random-effects model.
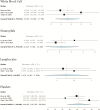
Results: Twenty-four studies (136 women) were included. The most common symptoms were fever (62.9%) and cough (36.8%). Laboratory findings included elevated C-reactive protein (57%) and lymphocytopenia (50%). Ground-glass opacity was the most common radiological finding (81.7%). Preterm birth rate was 37.7% and cesarean delivery rate was 76%. There was 1 maternal death. There were 2 fetal COVID-19 cases.
Conclusions: The clinical picture in pregnant women with COVID-19 did not differ from the nonpregnant population; however, the rate of preterm birth and cesarean delivery are considerably higher than international averages.
Keywords: coronavirus; neonates; pregnant; transmission.
© The Author(s) 2020. Published by Oxford University Press for the Infectious Diseases Society of America. All rights reserved. For permissions, e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures




Comment in
-
Letter to editor regarding "Clinical Presentation and Outcomes of Pregnant Women With Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis".Clin Infect Dis. 2022 Apr 9;74(7):1319. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciab690. Clin Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 34357380 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Reply to Wu, et al.Clin Infect Dis. 2022 Apr 9;74(7):1319-1320. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciab694. Clin Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 34358318 No abstract available.
References
-
- World Health Organization. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) outbreak Available at: https://www.who.int. Accessed 25 April 2020.
-
- World Health Organization. Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) situation report 154 Available at: https://www.who.int/docs/default-source/coronaviruse/situation-reports/2.... Accessed 22 June 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

