Esters of Glucose-2-Phosphate: Occurrence and Chemistry
- PMID: 32575421
- PMCID: PMC7356202
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25122829
Esters of Glucose-2-Phosphate: Occurrence and Chemistry
Abstract
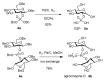
Phosphodiesters of glucose-2-phosphate (G2P) are found only in few natural compounds such as agrocinopine D and agrocin 84. Agrocinopine D is a G2P phosphodiester produced by plants infected by Agrobacterium fabrum C58 and recognized by the bacterial periplasmic binding protein AccA for being transported into the bacteria before cleavage by the phosphodiesterase AccF, releasing G2P, which promotes virulence by binding the repressor protein AccR. The G2P amide agrocin 84 is a natural antibiotic produced by the non-pathogenic Agrobacterium radiobacter K84 strain used as a biocontrol agent by competing with Agrobacterium fabrum C58. G2P esters are also found in irregular glycogen structures. The rare glucopyranosyl-2-phophoryl moiety found in agrocin 84 is the key structural signature enabling its action as a natural antibiotic. Likewise, G2P and G2P esters can also dupe the Agrobacterium agrocinopine catabolism cascade. Such observations illustrate the importance of G2P esters on which we have recently focused our interest. After a brief review of the reported phosphorylation coupling methods and the choice of carbohydrate building blocks used in G2P chemistry, a flexible access to glucose-2-phosphate esters using the phosphoramidite route is proposed.
Keywords: Agrobacterium fabrum; agrocin 84; agrocinopine; glucose-2-phosphate; phosphodiesters.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Ellis J.G., Kerr A., Petit A., Tempe J. Conjugal transfer of nopaline and agropine Ti-plasmids-the role of agrocinopines. Mol. Gen. Genet. 1982;186:269–274. doi: 10.1007/BF00331861. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

