Modulation of Endothelial Glycocalyx and Microcirculation in Healthy Young Men during High-Intensity Sprint Interval Cycling-Exercise by Supplementation with Pomegranate Extract. A Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 32575441
- PMCID: PMC7344862
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph17124405
Modulation of Endothelial Glycocalyx and Microcirculation in Healthy Young Men during High-Intensity Sprint Interval Cycling-Exercise by Supplementation with Pomegranate Extract. A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
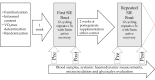
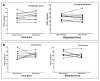
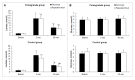
The natural components of the pomegranate fruit may provide additional benefits for endothelial function and microcirculation. It was hypothesized that supplementation with pomegranate extract might improve glycocalyx properties and microcirculation during acute high-intensity sprint interval cycling exercise. Eighteen healthy and recreationally active male volunteers 22-28 years of age were recruited randomly to the experimental and control groups. The experimental group was supplemented with pomegranate extract 20 mL (720 mg phenolic compounds) for two weeks. At the beginning and end of the study, the participants completed a high-intensity sprint interval cycling-exercise protocol. The microcirculation flow and density parameters, glycocalyx markers, systemic hemodynamics, lactate, and glucose concentration were evaluated before and after the initial and repeated (after 2 weeks supplementation) exercise bouts. There were no significant differences in the microcirculation or glycocalyx over the course of the study (p < 0.05). The lactate concentration was significantly higher in both groups after the initial and repeated exercise bouts, and were significantly higher in the experimental group compared to the control group after the repeated bout: 13.2 (11.9-14.8) vs. 10.3 (9.3-12.7) mmol/L, p = 0.017. Two weeks of supplementation with pomegranate extract does not influence changes in the microcirculation and glycocalyx during acute high-intensity sprint interval cycling-exercise. Although an unexplained rise in blood lactate concentration was observed.
Keywords: glycocalyx; microcirculation; polyphenols; sprint exercise.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Distinct Effects of Repeated-Sprint Training in Normobaric Hypoxia and β-Alanine Supplementation.J Am Coll Nutr. 2019 Feb;38(2):149-161. doi: 10.1080/07315724.2018.1475269. Epub 2018 Oct 2. J Am Coll Nutr. 2019. PMID: 30277420 Clinical Trial.
-
Moderate-intensity endurance training improves endothelial glycocalyx layer integrity in healthy young men.Exp Physiol. 2017 Jan 1;102(1):70-85. doi: 10.1113/EP085887. Exp Physiol. 2017. PMID: 27748983
-
Effects of high-intensity interval training on microvascular glycocalyx and associated microRNAs.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2019 Jun 1;316(6):H1538-H1551. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00751.2018. Epub 2019 Apr 12. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30978133
-
Effects of pomegranate extract on blood flow and vessel diameter after high-intensity exercise in young, healthy adults.Eur J Sport Sci. 2017 Apr;17(3):317-325. doi: 10.1080/17461391.2016.1230892. Epub 2016 Sep 20. Eur J Sport Sci. 2017. PMID: 27644475 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of pomegranate supplementation on exercise performance and post-exercise recovery in healthy adults: a systematic review.Br J Nutr. 2018 Dec;120(11):1201-1216. doi: 10.1017/S0007114518002696. Epub 2018 Oct 23. Br J Nutr. 2018. PMID: 30350760
Cited by
-
The role of hyaluronan in endothelial glycocalyx and potential preventative lifestyle strategy with advancing age.Curr Top Membr. 2023;91:139-156. doi: 10.1016/bs.ctm.2023.02.006. Epub 2023 Mar 10. Curr Top Membr. 2023. PMID: 37080678 Free PMC article.
-
The Effects of Pomegranate Supplementation on Markers of Exercise-Induced Muscle Damage: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Curr Dev Nutr. 2025 Jan 28;9(2):104560. doi: 10.1016/j.cdnut.2025.104560. eCollection 2025 Feb. Curr Dev Nutr. 2025. PMID: 40034870 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Asgary S., Sahebkar A., Afshani M.R., Keshvari M., Haghjooyjavanmard S., Rafieian-Kopaei M. Clinical evaluation of blood pressure lowering, endothelial function improving, hypolipidemic and anti-inflammatory effects of pomegranate juice in hypertensive subjects. Phytother. Res. 2014;28:193–199. doi: 10.1002/ptr.4977. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

