Micro/Nanoscale Structured Superhydrophilic and Underwater Superoleophobic Hybrid-Coated Mesh for High-Efficiency Oil/Water Separation
- PMID: 32575503
- PMCID: PMC7361680
- DOI: 10.3390/polym12061378
Micro/Nanoscale Structured Superhydrophilic and Underwater Superoleophobic Hybrid-Coated Mesh for High-Efficiency Oil/Water Separation
Abstract
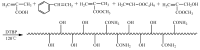
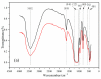
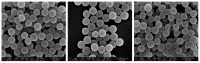
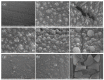
A novel micro/nanoscale rough structured superhydrophilic hybrid-coated mesh that shows underwater superoleophobic behavior is fabricated by spray casting or dipping nanoparticle-polymer suspensions on stainless steel mesh substrates. Water droplets can spread over the mesh completely; meanwhile, oil droplets can roll off the mesh at low tilt angles without any penetration. Besides overcoming the oil-fouling problem of many superhydrophilic coatings, this superhydrophilic and underwater superoleophobic mesh can be used to separate oil and water. The simple method used here to prepare the organic-inorganic hybrid coatings successfully produced controllable micro-nano binary roughness and also achieved a rough topography of micro-nano binary structure by controlling the content of inorganic particles. The mechanism of oil-water separation by the superhydrophilic and superoleophobic membrane is rationalized by considering capillary mechanics. Tetraethyl orathosilicate (TEOS) as a base was used to prepare the nano-SiO2 solution as a nano-dopant through a sol-gel process, while polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) was used as the film binder and glutaraldehyde as the cross-linking agent; the mixture was dip-coated on the surface of 300-mesh stainless steel mesh to form superhydrophilic and underwater superoleophobic film. Properties of nano-SiO2 represented by infrared spectroscopy and surface topography of the film observed under scanning electron microscope (SEM) indicated that the film surface had a coarse micro-nano binary structure; the effect of nano-SiO2 doping amount on the film's surface topography and the effect of such surface topography on hydrophilicity of the film were studied; contact angle of water on such surface was tested as 0° by the surface contact angle tester and spread quickly; the underwater contact angle to oil was 158°, showing superhydrophilic and underwater superoleophobic properties. The effect of the dosing amount of cross-linking agent to the waterproof swelling property and the permeate flux of the film were studied; the oil-water separation effect of the film to oil-water suspension and oil-water emulsion was studied too, and in both cases the separation efficiency reached 99%, which finally reduced the oil content to be lower than 50 mg/L. The effect of filtration times to permeate flux was studied, and it was found that the more hydrophilic the film was, the stronger the stain resistance would be, and the permeate flux would gradually decrease along with the increase of filtration times.
Keywords: coated mesh; micro-nanoscale binary rough structure; oil–water separation; superhydrophilic; underwater superoleophobic.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
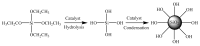









Similar articles
-
Efficient removal of oil from oil contaminated water by superhydrophilic and underwater superoleophobic nano/micro structured TiO2 nanofibers coated mesh.Chemosphere. 2017 Mar;171:134-141. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.12.031. Epub 2016 Dec 10. Chemosphere. 2017. PMID: 28013074
-
Study of factors governing oil-water separation process using TiO₂ films prepared by spray deposition of nanoparticle dispersions.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2014 Aug 27;6(16):13422-9. doi: 10.1021/am501867b. Epub 2014 Aug 7. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2014. PMID: 25058802
-
Air superhydrophilic-superoleophobic SiO2-based coatings for recoverable oil/water separation mesh with high flux and mechanical stability.J Colloid Interface Sci. 2021 Oct 15;600:118-126. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2021.05.004. Epub 2021 May 5. J Colloid Interface Sci. 2021. PMID: 34010769
-
Nacre-inspired underwater superoleophobic films with high transparency and mechanical robustness.Nat Protoc. 2022 Nov;17(11):2647-2667. doi: 10.1038/s41596-022-00725-3. Epub 2022 Aug 15. Nat Protoc. 2022. PMID: 35970874 Review.
-
Polyimide based super-wettable membranes/materials for high performance oil/water mixture and emulsion separation: A review.Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2021 Nov;297:102525. doi: 10.1016/j.cis.2021.102525. Epub 2021 Sep 23. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2021. PMID: 34653904 Review.
Cited by
-
Urushiol-Based Coating with High Surface Hydrophilicity for Easy-Cleaning of Oil Pollutants.Polymers (Basel). 2024 Nov 30;16(23):3392. doi: 10.3390/polym16233392. Polymers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39684137 Free PMC article.
-
Double cross-linked transparent superhydrophilic coating capable of anti-fogging even after abrasion and boiling.RSC Adv. 2023 Aug 4;13(34):23409-23418. doi: 10.1039/d3ra03113f. eCollection 2023 Aug 4. RSC Adv. 2023. PMID: 37546216 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cabrera J., Rojas G., Accorso N., Lizarraga L., Negri R. Membranes based on polyacrylamide coatings on metallic meshes prepared by a two-steps redox polymerization. Performance for oil-water separation and biofouling effects. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2020;247:116966. doi: 10.1016/j.seppur.2020.116966. - DOI
-
- Zhong X., Lv Z., Hu H., Jiang X., Fu H. Bio-based coatings with liquid repellency for various applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2020;382:123042. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.123042. - DOI
-
- Xue Z., Cao Y., Liu N., Feng L., Jiang L. Special wettable materials for oil/water separation. J. Mater. Chem. A. 2014;2:2445–2460. doi: 10.1039/C3TA13397D. - DOI
Grants and funding
- 21808070, 51673075/National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 201803030003, 201704030085/the Science & Technology Program of Guangzhou City
- 2018A030310349/the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province
- GC201813/the Research Fund Program of Guangdong Provincial Key Lab of Green Chemical Product Technology
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

