ESR Method in Monitoring of Nanoparticle Endocytosis in Cancer Cells
- PMID: 32575638
- PMCID: PMC7352947
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21124388
ESR Method in Monitoring of Nanoparticle Endocytosis in Cancer Cells
Abstract
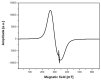
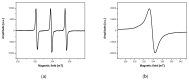
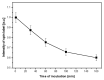
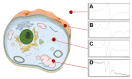
Magnetic nanoparticles are extensively studied for their use in diagnostics and medical therapy. The behavior of nanoparticles after adding them to cell culture is an essential factor (i.e., whether they attach to a cell membrane or penetrate the membrane and enter into the cell). The present studies aimed to demonstrate the application of electron spin resonance (ESR) as a suitable technique for monitoring of nanoparticles entering into cells during the endocytosis process. The model nanoparticles were composed of magnetite iron (II, III) oxide core functionalized with organic unit containing nitroxide radical 4-hydroxy-TEMPO (TEMPOL). The research studies included breast cancer cells, as well as model yeast and human microvascular endothelial cells. The results confirmed that the ESR method is suitable for studying the endocytosis process of nanoparticles in the selected cells. It also allows for direct monitoring of radical cellular processes.
Keywords: TEMPOL spin label; breast cancer cells; electron spin resonance; magnetic nanoparticles.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures









References
-
- Brzeziński M., Wedepohl S., Kost B., Calderón M. Nanoparticles from supramolecular polylactides overcome drug resistance of cancer cells. Eur. Polym. J. 2018;109:117–123. doi: 10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2018.08.060. - DOI
-
- Vong L.B., Bui T.Q., Tomita T., Sakamoto H., Hiramatsu Y., Nagasaki Y. Novel angiogenesis therapeutics by redox injectable hydrogel—Regulation of local nitric oxide generation for effective cardiovascular therapy. Biomaterials. 2018;167:143–152. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2018.03.023. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Nagasaki Y. Design and application of redox polymers for nanomedicine. Polym. J. 2018;50:821–836. doi: 10.1038/s41428-018-0054-6. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

