Serum metabolites reflecting gut microbiome alpha diversity predict type 2 diabetes
- PMID: 32576065
- PMCID: PMC7524143
- DOI: 10.1080/19490976.2020.1778261
Serum metabolites reflecting gut microbiome alpha diversity predict type 2 diabetes
Abstract
Type 2 diabetes (T2D) is associated with reduced gut microbiome diversity, although the cause is unclear. Metabolites generated by gut microbes also appear to be causative factors in T2D. We therefore searched for serum metabolites predictive of gut microbiome diversity in 1018 females from TwinsUK with concurrent metabolomic profiling and microbiome composition. We generated a Microbial Metabolites Diversity (MMD) score of six circulating metabolites that explained over 18% of the variance in microbiome alpha diversity. Moreover, the MMD score was associated with a significantly lower odds of prevalent (OR[95%CI] = 0.22[0.07;0.70], P = .01) and incident T2D (HR[95%CI] = 0.31[0.11,0.90], P = .03). We replicated our results in 1522 individuals from the ARIC study (prevalent T2D: OR[95%CI] = 0.79[0.64,0.96], P = .02, incident T2D: HR[95%CI] = 0.87[0.79,0.95], P = .003). The MMD score mediated 28%[15%,94%] of the total effect of gut microbiome on T2D after adjusting for confounders. Metabolites predicting higher microbiome diversity included 3-phenylpropionate(hydrocinnamate), indolepropionate, cinnamoylglycine and 5-alpha-pregnan-3beta,20 alpha-diol monosulfate(2) of which indolepropionate and phenylpropionate have already been linked to lower incidence of T2D. Metabolites correlating with lower microbial diversity included glutarate and imidazole propionate, of which the latter has been implicated in insulin resistance. Our results suggest that the effect of gut microbiome diversity on T2D is largely mediated by microbial metabolites, which might be modifiable by diet.
Keywords: Microbial metabolites; incident diabetes; microbiome diversity; prevalent diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
RPM is employee of Metabolon, Inc. TDS is co-founder of Zoe Global Ltd. AMV is a consultant for Zoe Global Ltd. All other authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
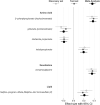
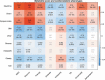

References
-
- Finucane MM, Stevens GA, Cowan MJ, Danaei G, Lin JK, Paciorek CJ, Singh GM, Gutierrez HR, Lu Y, Bahalim AN, et al. National, regional, and global trends in body-mass index since 1980: systematic analysis of health examination surveys and epidemiological studies with 960 country-years and 9.1 million participants. Lancet. 2011;377(9765):557–567. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(10)62037-5. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Forslund K, Hildebrand F, Nielsen T, Falony G, Le Chatelier E, Sunagawa S, Prifti E, Vieira-Silva S, Gudmundsdottir V, Pedersen HK, et al. Disentangling type 2 diabetes and metformin treatment signatures in the human gut microbiota. Nature. 2015;528(7581):262–266. doi:10.1038/nature15766. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- MR/N01183X/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- K24 HL152440/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG009974/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- K01 DK107782/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004402/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- MR/M016560/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- HHSN268201700002C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MR/M004422/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 HL142003/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201700003I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL149683/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 HL143089/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- DH_/Department of Health/United Kingdom
- SP/14/8/31352/BHF_/British Heart Foundation/United Kingdom
- HHSN268201700001I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- MR/N030125/1/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- HHSN268201700004I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201700005C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201700001C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201700003C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL141824/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201700004C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- HHSN268201700002I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201700005I/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
