Raising rare disease awareness using red flags, role play simulation and patient educators: results of a novel educational workshop on Raynaud phenomenon and systemic sclerosis
- PMID: 32576213
- PMCID: PMC7310378
- DOI: 10.1186/s13023-020-01439-z
Raising rare disease awareness using red flags, role play simulation and patient educators: results of a novel educational workshop on Raynaud phenomenon and systemic sclerosis
Abstract
Background: As lack of awareness of rare diseases (RDs) among healthcare professionals results in delayed diagnoses, there is a need for a more efficient approach to RD training during academic education. We designed an experimental workshop that used role-play simulation with patient educators and focused on teaching "red flags" that should raise the suspicion of an RD when faced with a patient with frequently encountered symptoms. Our objective was to report our experience, and to assess the improvement in learners' knowledge and the satisfaction levels of the participants.
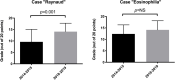
Results: The workshop consisted of 2 simulated consultations that both started with the same frequent symptom (Raynaud phenomenon, RP) but led to different diagnoses: a frequent condition (idiopathic RP) and an RD (systemic sclerosis, SSc). In the second simulated consultation, the role of the patient was played by a patient educator with SSc. By juxtaposing 2 seemingly similar situations, the training particularly highlighted the elements that help differentiate SSc from idiopathic RP. When answering a clinical case exam about RP and SSc, students that had participated in the workshop had a higher mean mark than those who had not (14 ± 3.7 vs 9.6 ± 5.5 points out of 20, p = 0.001). Participants mostly felt "very satisfied" with this training (94%), and "more comfortable" about managing idiopathic RP and SSc (100%). They considered the workshop "not very stressful" and "very formative" (both 71%). When asked about the strengths of this training, they mentioned the benefits of being put in an immersive situation, allowing a better acquisition of practical skills and a more interactive exchange with teachers, as well as the confrontation with a real patient, leading to a better retention of semiological findings and associating a relational component with this experience.
Conclusions: Through the use of innovative educational methods, such as role-play simulation and patient educators, and by focusing on teaching "red flags", our workshop successfully improved RP and SSc learning in a way that satisfied students. By modifying the workshop's scenarios, its template can readily be applied to other clinical situations, making it an interesting tool to teach other RDs.
Keywords: Big data; Medical education; Patient educators; Rare diseases; Raynaud phenomenon; Role play; Simulated patients; Simulation; Systemic sclerosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests in relation to this work.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Hyperspectral imaging in systemic sclerosis-associated Raynaud phenomenon.Arthritis Res Ther. 2023 Jan 20;25(1):10. doi: 10.1186/s13075-023-02990-3. Arthritis Res Ther. 2023. PMID: 36670487 Free PMC article.
-
Student and educator experiences of maternal-child simulation-based learning: a systematic review of qualitative evidence protocol.JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015 Jan;13(1):14-26. doi: 10.11124/jbisrir-2015-1694. JBI Database System Rev Implement Rep. 2015. PMID: 26447004
-
Factors Influencing Raynaud Condition Score Diary Outcomes in Systemic Sclerosis.J Rheumatol. 2019 Oct;46(10):1326-1334. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.180818. Epub 2019 Mar 1. J Rheumatol. 2019. PMID: 30824643
-
From Raynaud's Phenomenon to Very Early Diagnosis of Systemic Sclerosis- The VEDOSS approach.Curr Rheumatol Rev. 2013;9(4):245-8. doi: 10.2174/157339710904140417124819. Curr Rheumatol Rev. 2013. PMID: 26932288 Review.
-
Raynaud phenomenon and digital ulcers in systemic sclerosis.Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2020 Apr;16(4):208-221. doi: 10.1038/s41584-020-0386-4. Epub 2020 Feb 25. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2020. PMID: 32099191 Review.
Cited by
-
Beliefs, screening attitudes and breast cancer awareness of young women with neurofibromatosis type 1: A reflexive thematic analysis.J Health Psychol. 2025 Mar;30(3):369-383. doi: 10.1177/13591053241255053. Epub 2024 Jun 10. J Health Psychol. 2025. PMID: 38859614 Free PMC article.
-
Rare disease education in Europe and beyond: time to act.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2022 Dec 19;17(1):441. doi: 10.1186/s13023-022-02527-y. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2022. PMID: 36536417 Free PMC article.
-
Barriers to care in juvenile localized and systemic scleroderma: an exploratory survey study of caregivers' perspectives.Pediatr Rheumatol Online J. 2023 Apr 25;21(1):39. doi: 10.1186/s12969-023-00819-6. Pediatr Rheumatol Online J. 2023. PMID: 37098622 Free PMC article.
-
Big Data for Biomedical Education with a Focus on the COVID-19 Era: An Integrative Review of the Literature.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Aug 26;18(17):8989. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18178989. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34501581 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Iranian future healthcare professionals' knowledge and opinions about rare diseases: cross-sectional study.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2022 Sep 29;17(1):366. doi: 10.1186/s13023-022-02458-8. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2022. PMID: 36175905 Free PMC article.
References
-
- European Union Committee of Experts on Rare Diseases (EUCERD) 2014 report on the state of the art of rare disease activities in Europe. 2014.
-
- Donnart A, Viollet V, Roinet-Tournay M. Rare diseases, a public health issue. Soins Pediatr Pueric. 2013;1:17–19. - PubMed
-
- European Organisation for Rare Diseases (EURORDIS) Survey of the delay in diagnosis for 8 rare diseases in Europe (‘EURODISCARE 2’): fact sheet. 2007.
-
- European Organisation for Rare Diseases (EURORDIS) The voice of 12,000 patients: experiences and expectations of rare disease patients on diagnosis and Care in Europe - a report based on the EurordisCare2 and EurordisCare3 surveys. 2009.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

