Early detection of parenting stress in mothers of preterm infants during their first-year home
- PMID: 32576260
- PMCID: PMC7313173
- DOI: 10.1186/s40359-020-00435-z
Early detection of parenting stress in mothers of preterm infants during their first-year home
Abstract
Background: Maternal stress following the birth of an infant is well acknowledged. It is particularly so when infants are born prematurely as their mothers cannot fully take on their parenting role until their infant(s) is discharged from neonatal intensive care units (NICUs). In this exploratory study, we examined whether these mothers' parenting stress would lessen during their first-year reunification with their infant(s) as they settle into motherhood at home.
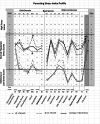
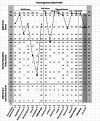
Methods: Two groups of mothers with infants born between 24- and 33-week gestational age were recruited. A group of 25 mothers were monitored at their infants' 1-month corrected age (CA) and a second group of 24 mothers were monitored at their infants' 12-month CA. Subjects completed the long form Parental Stress Index (PSI) ranking how stressful they perceive the individual subscales in the Child and Parent Domains of the self-reported questionnaire (PSI-3; Abidin; PAR Inc). The PSI theorizes that the stress mothers perceive is a resultant of their respective characteristics, interactions with their infant(s), family, and environment. Statistical analyses include descriptive statistics, χ2 square analysis, and independent t-test.
Results: There was no significant difference in the levels of perceived stress in the PSI subscales between the two groups of mothers at 1- and 12-month CA. Scores for the majority of respondents fell within the 15th to 80th percentile (% ile) distribution of Abidin's normative population, with some mothers falling below the 15th % ile.
Discussion/conclusion: The data collected suggest that: 1. the perceived stress experienced by mothers during their first-year reunited with their preterm infants is within the normal range observed in Abidin's normative population. 2. As the PSI is a self-reported survey, care providers need to be aware that some mothers may downplay their stress responses. 3. With the ability to monitor individual participants, the PSI can be readily offered to mothers at their infants' first year routine clinical visits to assist in the early identification of parenting issues that may threaten the development of a healthy mother-infant dyad. Early appropriate guidance and social support would help "at-risk" mothers develop more constructive parenting routines.
Keywords: Maternal stress perception; Parenting[al] Stress Index [stress index]; Preterm mother-infant dyad.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have sole responsibility for all parts of the manuscript and have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Use of the parenting stress index in mothers of preterm infants.Adv Neonatal Care. 2004 Feb;4(1):33-41. doi: 10.1016/j.adnc.2003.11.012. Adv Neonatal Care. 2004. PMID: 14988878
-
Relation between sleep status of preterm infants aged 1-2 years and mothers' parenting stress.Pediatr Int. 2013 Aug;55(4):416-21. doi: 10.1111/ped.12097. Epub 2013 Jun 6. Pediatr Int. 2013. PMID: 23480660
-
Early intervention program reduces stress in parents of preterms during childhood, a randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2014 Oct 4;15:387. doi: 10.1186/1745-6215-15-387. Trials. 2014. PMID: 25282345 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Family Nurture Intervention and mother-preterm infant autonomic emotional connection in the neonatal intensive care unit: A review.Acta Paediatr. 2025 Apr;114(4):760-771. doi: 10.1111/apa.17456. Epub 2024 Nov 3. Acta Paediatr. 2025. PMID: 39491338 Review.
-
Early Intervention for Preterm Infants and Their Mothers: A Systematic Review.J Perinat Neonatal Nurs. 2021 Oct-Dec 01;35(4):E69-E82. doi: 10.1097/JPN.0000000000000065. J Perinat Neonatal Nurs. 2021. PMID: 25408293
Cited by
-
Stress, postpartum depression, and anxiety in mothers of neonates admitted in the NICU: A cross-sectional hospital-based study.Ind Psychiatry J. 2023 Jan-Jun;32(1):48-58. doi: 10.4103/ipj.ipj_93_22. Epub 2022 Dec 9. Ind Psychiatry J. 2023. PMID: 37274566 Free PMC article.
-
Stress and its associated factors in mothers with preterm infants in a private tertiary care hospital of Karachi, Pakistan: an analytical cross-sectional study.BMJ Open. 2024 Nov 20;14(11):e091117. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-091117. BMJ Open. 2024. PMID: 39572097 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of parental stress in neonatal intensive care unit in Iran: a national study.BMC Nurs. 2023 Feb 15;22(1):41. doi: 10.1186/s12912-023-01200-4. BMC Nurs. 2023. PMID: 36788549 Free PMC article.
-
The Effect of Applying Problem-solving Skills on Stress Coping Styles and Emotional Self-efficacy in Mothers of Preterm Neonates: A Randomized Clinical Trial.Int J Community Based Nurs Midwifery. 2024 Oct 1;12(4):254-266. doi: 10.30476/ijcbnm.2024.100522.2368. eCollection 2024 Oct. Int J Community Based Nurs Midwifery. 2024. PMID: 39411569 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Psychosocial stress factors in families with preterm infants during the Covid-19 pandemic: a cross-sectional study.Child Adolesc Psychiatry Ment Health. 2025 Apr 4;19(1):41. doi: 10.1186/s13034-025-00890-9. Child Adolesc Psychiatry Ment Health. 2025. PMID: 40186315 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lau C, Henning SJ. Mutualism in mother-offspring interaction: its importance in the regulation of milk release. In: Meisami E, Timiras P, editors. Handbook of human growth and developmental biology. Boca Raton: CRC Press, Inc; 1990. pp. 195–216.
-
- Brazelton TB, Tronick E, Adamson L, Als H, Wise S. Early mother-infant reciprocity. CIBA Found Symp. 1975;33:137–154. - PubMed
-
- Viaux-Savelon S, Rosenblum O, Guedeney A, Diene G, Cabal-Berthoumieu S, Fichaux-Bourin P, Molinas C, Faye S, Valette M, Bascoul C, et al. Dyssynchrony and perinatal psychopathology impact of child disease on parents-child interactions, the paradigm of Prader Willi syndrom. J Physiol Paris. 2016;110(4 Pt B):427–433. - PubMed
-
- Kendrick KM. Oxytocin, motherhood and bonding. Exp Physiol. 2000;85:111S–124S. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

