Erwinia carotovora Quorum Sensing System Regulates Host-Specific Virulence Factors and Development Delay in Drosophila melanogaster
- PMID: 32576677
- PMCID: PMC7315124
- DOI: 10.1128/mBio.01292-20
Erwinia carotovora Quorum Sensing System Regulates Host-Specific Virulence Factors and Development Delay in Drosophila melanogaster
Abstract
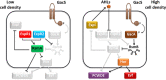
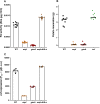
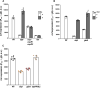
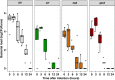
Multihost bacteria have to rapidly adapt to drastic environmental changes, relying on a fine integration of multiple stimuli for an optimal genetic response. Erwinia carotovora spp. are phytopathogens that cause soft-rot disease. Strain Ecc15 in particular is a model for bacterial oral-route infection in Drosophila melanogaster as it harbors a unique gene, evf, that encodes the Erwinia virulence factor (Evf), which is a major determinant for infection of the D. melanogaster gut. However, the factors involved in the regulation of evf expression are poorly understood. We investigated whether evf could be controlled by quorum sensing as, in the Erwinia genus, quorum sensing regulates pectolytic enzymes, the major virulence factors needed to infect plants. Here, we show that transcription of evf is positively regulated by quorum sensing in Ecc15 via acyl-homoserine lactone (AHL) signal synthase ExpI and AHL receptors ExpR1 and ExpR2. We also show that the load of Ecc15 in the gut depends upon the quorum sensing-mediated regulation of evf Furthermore, we demonstrate that larvae infected with Ecc15 suffer a developmental delay as a direct consequence of the regulation of evf via quorum sensing. Finally, we demonstrate that evf is coexpressed with plant cell wall-degrading enzymes (PCWDE) during plant infection in a quorum sensing-dependent manner. Overall, our results show that Ecc15 relies on quorum sensing to control production of both pectolytic enzymes and Evf. This regulation influences the interaction of Ecc15 with its two known hosts, indicating that quorum sensing signaling may impact bacterial dissemination via insect vectors that feed on rotting plants.IMPORTANCE Integration of genetic networks allows bacteria to rapidly adapt to changing environments. This is particularly important in bacteria that interact with multiple hosts. Erwinia carotovora is a plant pathogen that uses Drosophila melanogaster as a vector. To interact with these two hosts, Ecc15 uses different sets of virulence factors: plant cell wall-degrading enzymes to infect plants and the Erwinia virulence factor (evf) to infect Drosophila Our work shows that, despite the virulence factors being specific for each host, both sets are coactivated by homoserine lactone quorum sensing and by the two-component GacS/A system in infected plants. This regulation is essential for Ecc15 loads in the gut of Drosophila and minimizes the developmental delay caused by the bacteria with respect to the insect vector. Our findings provide evidence that coactivation of the host-specific factors in the plant may function as a predictive mechanism to maximize the probability of transit of the bacteria between hosts.
Keywords: Drosophila; Ecc15; bacterial infections; homoserine lactones; host-pathogen interactions; insect development; invertebrate-microbe interactions; quorum sensing.
Copyright © 2020 Vieira et al.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Signal Integration in Quorum Sensing Enables Cross-Species Induction of Virulence in Pectobacterium wasabiae.mBio. 2017 May 23;8(3):e00398-17. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00398-17. mBio. 2017. PMID: 28536283 Free PMC article.
-
Evf, a virulence factor produced by the Drosophila pathogen Erwinia carotovora, is an S-palmitoylated protein with a new fold that binds to lipid vesicles.J Biol Chem. 2009 Feb 6;284(6):3552-62. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M808334200. Epub 2008 Nov 1. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 18978353
-
Erwinia carotovora Evf antagonizes the elimination of bacteria in the gut of Drosophila larvae.Cell Microbiol. 2007 Jan;9(1):106-19. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-5822.2006.00771.x. Epub 2006 Jul 31. Cell Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 16879453
-
Quorum sensing and expression of virulence in pectobacteria.Sensors (Basel). 2012;12(3):3327-49. doi: 10.3390/s120303327. Epub 2012 Mar 8. Sensors (Basel). 2012. PMID: 22737011 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Quorum sensing, virulence and secondary metabolite production in plant soft-rotting bacteria.Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2007 Jul 29;362(1483):1165-83. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2007.2042. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2007. PMID: 17360277 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Gut Bacterial Diversity in Different Life Cycle Stages of Adelphocoris suturalis (Hemiptera: Miridae).Front Microbiol. 2021 Jun 2;12:670383. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.670383. eCollection 2021. Front Microbiol. 2021. PMID: 34149656 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro and in vivo selection and cost of bacteriophage resistance on natural Escherichia coli.Microlife. 2025 Aug 11;6:uqaf017. doi: 10.1093/femsml/uqaf017. eCollection 2025. Microlife. 2025. PMID: 40837842 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial Quorum-Sensing Regulation Induces Morphological Change in a Key Host Tissue during the Euprymna scolopes-Vibrio fischeri Symbiosis.mBio. 2021 Oct 26;12(5):e0240221. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02402-21. Epub 2021 Sep 28. mBio. 2021. PMID: 34579565 Free PMC article.
-
Quorum Sensing: Not Just a Bridge Between Bacteria.Microbiologyopen. 2025 Mar;14(1):e70016. doi: 10.1002/mbo3.70016. Microbiologyopen. 2025. PMID: 40159675 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Draft Genome Sequence Resource of Erwinia sp. Strain INIA01, a Phytopathogen Isolated from a Diseased Stalk of Peruvian Maize.Microbiol Resour Announc. 2023 May 17;12(5):e0012023. doi: 10.1128/mra.00120-23. Epub 2023 Apr 13. Microbiol Resour Announc. 2023. PMID: 37052494 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
