ADL-dependency, D-Dimers, LDH and absence of anticoagulation are independently associated with one-month mortality in older inpatients with Covid-19
- PMID: 32576712
- PMCID: PMC7343508
- DOI: 10.18632/aging.103583
ADL-dependency, D-Dimers, LDH and absence of anticoagulation are independently associated with one-month mortality in older inpatients with Covid-19
Abstract
Background: To assess factors associated with one-month mortality among older inpatients with Covid-19.
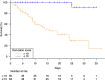
Results: The mean age was 78 ± 7.8 years, 55.5% were men, CT scan lung damage was observed in 76% of the patients (mild 23%, moderate 38%, extensive 22%, and severe 7%). The mortality rate was 26%. Dependency/Activities of Daily Living (ADL) score ≤ 5/6, D-Dimers, LDH, and no anticoagulation by reference for curative were independently associated with one-month mortality. A score derived from the multivariate model showed good calibration and very good discrimination (Harrell's C index [95%CI] = 0.83 [0.79-0.87]).
Conclusion: ADL-dependency, high serum levels of D-Dimers and LDH and the absence of anticoagulation were independently associated with one-month mortality among older inpatients with Covid-19.
Methods: 108 consecutive older inpatients aged 65 and over with Covid-19 confirmed by RT-PCR and/or typical CT chest scan were prospectively included in a French single-centre cohort study from March to April 2020. A systematic geriatric assessment was performed. Covariates were lymphocyte count, serum levels of albumin, C-Reactive Protein, D-Dimers and Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH), anticoagulation level, and exposure to the hydroxychloroquine and azithromycin combined therapy. Cox uni- and multivariate proportional-hazard regressions were performed to identify predictors of one-month mortality.
Keywords: COVID-19; anticoagulation; geriatric assessment; mortality; predictive biomarkers.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
IL-6-based mortality risk model for hospitalized patients with COVID-19.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2020 Oct;146(4):799-807.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2020.07.009. Epub 2020 Jul 22. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32710975 Free PMC article.
-
CURB-65 may serve as a useful prognostic marker in COVID-19 patients within Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study.Epidemiol Infect. 2020 Oct 1;148:e241. doi: 10.1017/S0950268820002368. Epidemiol Infect. 2020. PMID: 32998791 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 in the Healthy Patient Population: Demographic and Clinical Phenotypic Characterization and Predictors of In-Hospital Outcomes.Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2020 Nov;40(11):2764-2775. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.120.314845. Epub 2020 Sep 10. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2020. PMID: 32907371 Free PMC article.
-
Fibrinogen and D-dimer variances and anticoagulation recommendations in Covid-19: current literature review.Rev Assoc Med Bras (1992). 2020 Jun;66(6):842-848. doi: 10.1590/1806-9282.66.6.842. Epub 2020 Jul 20. Rev Assoc Med Bras (1992). 2020. PMID: 32696883 Review.
-
Lactate dehydrogenase levels predict coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) severity and mortality: A pooled analysis.Am J Emerg Med. 2020 Sep;38(9):1722-1726. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2020.05.073. Epub 2020 May 27. Am J Emerg Med. 2020. PMID: 32738466 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Major coagulation disorders and parameters in COVID-19 patients.Eur J Med Res. 2022 Feb 15;27(1):25. doi: 10.1186/s40001-022-00655-6. Eur J Med Res. 2022. PMID: 35168674 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of hydroxychloroquine with or without azithromycin on the mortality of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Clin Microbiol Infect. 2021 Jan;27(1):19-27. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2020.08.022. Epub 2020 Aug 26. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2021. PMID: 32860962 Free PMC article.
-
Lung ultrasound is a reliable diagnostic technique to predict abnormal CT chest scan and to detect oxygen requirements in COVID-19 pneumonia.Aging (Albany NY). 2020 Oct 30;12(20):19945-19953. doi: 10.18632/aging.104150. Epub 2020 Oct 30. Aging (Albany NY). 2020. PMID: 33136555 Free PMC article.
-
A Multimodal Approach for the Risk Prediction of Intensive Care and Mortality in Patients with COVID-19.Diagnostics (Basel). 2021 Dec 28;12(1):56. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics12010056. Diagnostics (Basel). 2021. PMID: 35054223 Free PMC article.
-
Discontinuity of social support among US adults with cognitive impairment before and after the confirmed diagnosis of dementia: a matched ambidirectional cohort study.BMC Med. 2025 Jul 15;23(1):428. doi: 10.1186/s12916-025-04264-y. BMC Med. 2025. PMID: 40665295 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous