Epstein-Barr Virus-related mucocutaneous ulcer lymphoma associated with Crohn's disease, treated with monoclonal antibody anti-CD30
- PMID: 32577242
- PMCID: PMC7303872
- DOI: 10.1002/ccr3.2721
Epstein-Barr Virus-related mucocutaneous ulcer lymphoma associated with Crohn's disease, treated with monoclonal antibody anti-CD30
Abstract
Epstein-Barr virus-related mucocutaneous ulcer lymphoma is a rare entity promoted by immunosuppression. It is less described in inflammatory bowel diseases, and mostly these are refractory diseases. CD30 acts to Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) local proliferation and thus could be an interesting target. Brentuximab vedotin could become a new helpful tool.
Keywords: CD30; brentuximab vedotin; epstein‐barr virus; immunosuppression; lymphoma.
© 2020 The Authors. Clinical Case Reports published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures
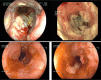
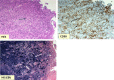

References
-
- Hart M, Thakral B, Yohe S, et al. EBV‐positive mucocutaneous ulcer in organ transplant recipients: a localized indolent posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorder. Am J Surg Pathol. 2014;38(11):1522‐1529. - PubMed
-
- Dierickx D, Habermann TM. Post‐transplantation lymphoproliferative disorders in adults. N Engl J Med. 2018;378(6):549‐562. - PubMed
-
- Nelson AA, Harrington AM, Kroft S, Dahar MA, Hamadani M, Dhakal B. Presentation and management of post‐allogeneic transplantation EBV‐positive mucocutaneous ulcer. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2016;51(2):300‐302. - PubMed
-
- Vase MØ, Maksten EF, Bendix K, et al. Occurrence and prognostic relevance of CD30 expression in post‐transplant lymphoproliferative disorders. Leuk Lymphoma. 2015;56(6):1677‐1685. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

