This is a preprint.
Structures of human antibodies bound to SARS-CoV-2 spike reveal common epitopes and recurrent features of antibodies
- PMID: 32577645
- PMCID: PMC7302198
- DOI: 10.1101/2020.05.28.121533
Structures of human antibodies bound to SARS-CoV-2 spike reveal common epitopes and recurrent features of antibodies
Update in
-
Structures of Human Antibodies Bound to SARS-CoV-2 Spike Reveal Common Epitopes and Recurrent Features of Antibodies.Cell. 2020 Aug 20;182(4):828-842.e16. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.06.025. Epub 2020 Jun 24. Cell. 2020. PMID: 32645326 Free PMC article.
Abstract
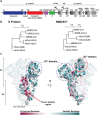
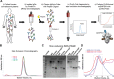
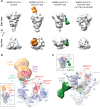
Neutralizing antibody responses to coronaviruses focus on the trimeric spike, with most against the receptor-binding domain (RBD). Here we characterized polyclonal IgGs and Fabs from COVID-19 convalescent individuals for recognition of coronavirus spikes. Plasma IgGs differed in their degree of focus on RBD epitopes, recognition of SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV, and mild coronaviruses, and how avidity effects contributed to increased binding/neutralization of IgGs over Fabs. Electron microscopy reconstructions of polyclonal plasma Fab-spike complexes showed recognition of both S1A and RBD epitopes. A 3.4Å cryo-EM structure of a neutralizing monoclonal Fab-S complex revealed an epitope that blocks ACE2 receptor-binding on "up" RBDs. Modeling suggested that IgGs targeting these sites have different potentials for inter-spike crosslinking on viruses and would not be greatly affected by identified SARS-CoV-2 spike mutations. These studies structurally define a recurrent anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibody class derived from VH3-53/VH3-66 and similarity to a SARS-CoV VH3-30 antibody, providing criteria for evaluating vaccine-elicited antibodies.
Keywords: COVID-19; Coronavirus; ELISA; Fab; IgG; MERS-CoV; SARS-CoV; SARS-CoV-2; convalescent plasma; electron microscopy.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


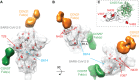
References
-
- Bianchi M., Turner H.L., Nogal B., Cottrell C.A., Oyen D., Pauthner M., Bastidas R., Nedellec R., McCoy L.E., Wilson I.A., et al. (2018). Electron-Microscopy-Based Epitope Mapping Defines Specificities of Polyclonal Antibodies Elicited during HIV-1 BG505 Envelope Trimer Immunization. Immunity 49, 288–300 e288. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Brouwer P.J.M., Caniels T.G., van der Straten K., Snitselaar J.L., Aldon Y., Bangaru S., Torres J.L., Okba N.M.A., Claireaux M., Kerster G., et al. (2020). Potent neutralizing antibodies from COVID-19 patients define multiple targets of vulnerability. bioRxiv 10.1101/2020.05.12.088716 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
