This is a preprint.
Long-term SARS-CoV-2 RNA Shedding and its Temporal Association to IgG Seropositivity
- PMID: 32577666
- PMCID: PMC7302207
- DOI: 10.1101/2020.06.02.20120774
Long-term SARS-CoV-2 RNA Shedding and its Temporal Association to IgG Seropositivity
Update in
-
Long-term SARS-CoV-2 RNA shedding and its temporal association to IgG seropositivity.Cell Death Discov. 2020 Dec 2;6(1):138. doi: 10.1038/s41420-020-00375-y. Cell Death Discov. 2020. PMID: 33298894 Free PMC article.
Abstract
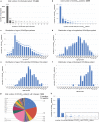
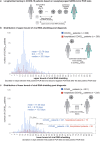
Analysis of 851 COVID-19 patients with a SARS-CoV-2-positive PCR at follow-up shows 99 patients remained SARS-CoV-2-positive after four weeks from initial diagnosis. Surprisingly, a majority of these long-term viral RNA shedders were not hospitalized (61 of 99), with variable PCR Crossing point values over the month post diagnosis. For the 851-patient cohort, the mean lower bound of viral RNA shedding was 17.3 days (SD: 7.8), and the mean upper bound of viral RNA shedding from 668 patients transitioning to confirmed PCR-negative status was 22.7 days (SD: 11.8). Among 104 patients with an IgG test result, 90 patients were seropositive to date, with mean upper bound of time to seropositivity from initial diagnosis being 37.8 days (95%CI: 34.3-41.3). Juxtaposing IgG/PCR tests revealed that 14 of 90 patients are non-hospitalized and seropositive yet shed viral RNA. This study emphasizes the need for monitoring viral loads and neutralizing antibody titers in long-term shedders.
Figures


References
-
- Johns Hopkins Coronavirus Resource Center. https://coronavirus.jhu.edu/
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
