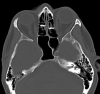
Isolated olfactory cleft involvement in SARS-CoV-2 infection: prevalence and clinical correlates
- PMID: 32577901
- PMCID: PMC7309200
- DOI: 10.1007/s00405-020-06165-7
Isolated olfactory cleft involvement in SARS-CoV-2 infection: prevalence and clinical correlates
Abstract
Purpose: Smell alterations are a symptom of COVID-19 and have been associated with olfactory cleft mucosal thickening (OCMT). Although their pathogenesis is unclear, evidences link them to viral neuroinvasive potential. This study aims at estimating the prevalence of OCMT in CT scans of COVID-19 patients and investigating its clinical correlates.
Methods: In a single-institution retrospective cross-sectional study, we included all patients hospitalized for COVID-19 undergoing head CT scan for any reason. Exclusion criteria were history of recent head trauma or chronic rhinosinusitis; opacification > 2 mm in any sinonasal space other than the olfactory cleft; CT performed during/after invasive ventilation or feeding via nasogastric tube. We recorded the prevalence of OCMT and related it to age, sex, need for invasive ventilation during hospital stay, outcome, length of hospital stay, diffusion of lung SARS-CoV-19 lesions and outcome.
Results: 63 eligible patients were identified (39 male, 24 female; median age 77.82 ± 17.77 years). OCMT was identified in 16 patients (25.4%; 95% CI 15.3-37.9%). Patients with OCMT had longer hospital stays (median 16 ± 4 vs. 9 ± 14.5 days, p = .009, Mann-Whitney U test) and required invasive ventilation more frequently than patients without mucosal thickening (OR 4.89, 95% CI 0.96-24.89, p = .063, Fisher's test). No other difference was observed.
Conclusion: OCMT affects nearly one in four patients hospitalized for COVID-19. It is associated with a worse disease course irrespective of age, sex and diffusion of lung lesions, although with no direct effect on survival.
Keywords: Coronavirus; Mucous membrane; Olfaction disorders; Smell; Viral tropism.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Olfactory Dysfunction and Sinonasal Symptomatology in COVID-19: Prevalence, Severity, Timing, and Associated Characteristics.Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020 Jul;163(1):114-120. doi: 10.1177/0194599820929185. Epub 2020 May 19. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020. PMID: 32423357 Free PMC article.
-
Olfactory Dysfunction in COVID-19 Patients: Prevalence and Prognosis for Recovering Sense of Smell.Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2021 Jan;164(1):82-86. doi: 10.1177/0194599820943530. Epub 2020 Jul 14. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2021. PMID: 32662745
-
A cross-sectional study of olfactory and taste disorders among COVID-19 patients in China.Mil Med Res. 2021 Sep 13;8(1):51. doi: 10.1186/s40779-021-00339-y. Mil Med Res. 2021. PMID: 34517915 Free PMC article.
-
The Importance of Considering Olfactory Dysfunction During the COVID-19 Pandemic and in Clinical Practice.J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2021 Jan;9(1):7-12. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2020.10.036. Epub 2020 Oct 28. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2021. PMID: 33130145 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aggregate Prevalence of Chemosensory and Sinonasal Dysfunction in SARS-CoV-2 and Related Coronaviruses.Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020 Jul;163(1):156-161. doi: 10.1177/0194599820929278. Epub 2020 May 19. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020. PMID: 32423285 Review.
Cited by
-
Olfactory and gustatory dysfunctions in SARS-CoV-2 infection: A systematic review.Brain Behav Immun Health. 2021 Aug;15:100268. doi: 10.1016/j.bbih.2021.100268. Epub 2021 May 18. Brain Behav Immun Health. 2021. PMID: 34027497 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Psychophysical evaluation of chemosensory functions 5 weeks after olfactory loss due to COVID-19: a prospective cohort study on 72 patients.Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2021 Jan;278(1):101-108. doi: 10.1007/s00405-020-06267-2. Epub 2020 Aug 4. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2021. PMID: 32754871 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical, sinonasal, and long-term smell and taste outcomes in mildly symptomatic COVID-19 patients.Int J Clin Pract. 2021 Jul;75(7):e14260. doi: 10.1111/ijcp.14260. Epub 2021 Apr 29. Int J Clin Pract. 2021. PMID: 33884722 Free PMC article.
-
Hospital length of stay for COVID-19 patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Multidiscip Respir Med. 2022 Aug 9;17(1):856. doi: 10.4081/mrm.2022.856. eCollection 2022 Jan 12. Multidiscip Respir Med. 2022. PMID: 36117876 Free PMC article.
-
The clinical course of smell and taste loss in COVID-19 hospitalized patients.Hippokratia. 2020 Apr-Jun;24(2):66-71. Hippokratia. 2020. PMID: 33488054 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lechien JR, Chiesa-Estomba CM, De Siati DR, Horoi M, Le Bon SD, Rodriguez A, et al. Olfactory and gustatory dysfunctions as a clinical presentation of mild-to-moderate forms of the coronavirus disease (COVID-19): a multicenter European study. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2020 doi: 10.1007/s00405-020-05965-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous