Validation of the Korean Version of the Bronchiectasis Health Questionnaire
- PMID: 32578411
- PMCID: PMC7362752
- DOI: 10.4046/trd.2020.0025
Validation of the Korean Version of the Bronchiectasis Health Questionnaire
Abstract
Background: The Bronchiectasis Health Questionnaire (BHQ) is a simple and repeatable, self-reporting health status questionnaire for bronchiectasis. We have translated the original version of the BHQ into Korean using a standardized methodology. The purpose of this study was to assess the validity of the Korean version of the BHQ (K-BHQ) with Korean patients.
Methods: Stable state patients with bronchiectasis from two academic hospitals were enrolled in this study. The validity was assessed by investigating the relationship between the K-BHQ scores and the Korean version of the Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Assessment Test (K-CAT) scores. We also investigated the relationship between the K-BHQ scores and other variables of the modified Medical Research Council's (mMRC) dyspnea scale, lung function, and exacerbations.
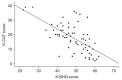
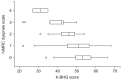
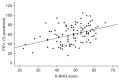
Results: A total of 126 patients with bronchiectasis were enrolled. The mean age was 64.3 (standard deviation [SD], 9.7). Women comprised 53.2% of the patients. The mean forced expiratory volume in one second (FEV1) was 60% of the predicted value (SD, 18.9%); the mean K-CAT score was 17.6 (SD, 9.1). The K-BHQ scores correlated strongly with the K-CAT scores (r=-0.656, p<0.001). There was significant correlation between the K-BHQ scores and the mMRC dyspnea scale (ρ=-0.409, p<0.001), FEV1 (r=0.406, p<0.001), and number of exacerbations requiring hospitalization (ρ=-0.303, p=0.001).
Conclusion: The K-BHQ is valid for assessing the health-related quality of life or health status of Korean bronchiectasis patients.
Keywords: Bronchiectasis Health Questionnaire; Validation; Bronchiectasis.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The development and validation of the Bronchiectasis Health Questionnaire.Eur Respir J. 2017 May 11;49(5):1601532. doi: 10.1183/13993003.01532-2016. Print 2017 May. Eur Respir J. 2017. PMID: 28495688
-
A study of the psychometric properties of the Brazilian...Portuguese version of Bronchiectasis Health Questionnaire.Pulmonology. 2023 Jan-Feb;29(1):42-49. doi: 10.1016/j.pulmoe.2020.10.012. Epub 2020 Dec 30. Pulmonology. 2023. PMID: 33386281
-
Validation of Korean Version of the London Chest Activity of Daily Living Scale in Patients With Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease.Ann Rehabil Med. 2018 Apr;42(2):329-335. doi: 10.5535/arm.2018.42.2.329. Epub 2018 Apr 30. Ann Rehabil Med. 2018. PMID: 29765887 Free PMC article.
-
Assessing effects of inhaled antibiotics in adults with non-cystic fibrosis bronchiectasis--experiences from recent clinical trials.Expert Rev Respir Med. 2018 Sep;12(9):769-782. doi: 10.1080/17476348.2018.1503540. Epub 2018 Aug 3. Expert Rev Respir Med. 2018. PMID: 30025482 Review.
-
Prevention of exacerbations in patients with stable non-cystic fibrosis bronchiectasis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of pharmacological and non-pharmacological therapies.BMJ Evid Based Med. 2018 Jun;23(3):96-103. doi: 10.1136/bmjebm-2018-110893. Epub 2018 Apr 20. BMJ Evid Based Med. 2018. PMID: 29678900
Cited by
-
The Validity and Reliability of the Turkish version of Modified Medical Research Council Dyspnea Scale in Systemic Sclerosis Patients with Interstitial Lung Disease.Thorac Res Pract. 2024 Nov 1;25(6):215-220. doi: 10.5152/ThoracResPract.2024.23135. Thorac Res Pract. 2024. PMID: 39511844 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of depression and its associated factors in bronchiectasis: findings from KMBARC registry.BMC Pulm Med. 2021 Sep 27;21(1):306. doi: 10.1186/s12890-021-01675-4. BMC Pulm Med. 2021. PMID: 34579692 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical Impacts of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Isolation in Patients with Bronchiectasis: Findings from KMBARC Registry.J Clin Med. 2024 Aug 24;13(17):5011. doi: 10.3390/jcm13175011. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39274224 Free PMC article.
-
Mucus plugging, disease severity and sputum myeloperoxidase concentration in bronchiectasis.ERJ Open Res. 2025 May 19;11(3):00279-2024. doi: 10.1183/23120541.00279-2024. eCollection 2025 May. ERJ Open Res. 2025. PMID: 40391060 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Is Associated With Decreased Quality of Life in Bronchiectasis Patients: Findings From the KMBARC Registry.Front Med (Lausanne). 2021 Aug 16;8:722124. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2021.722124. eCollection 2021. Front Med (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34490307 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Polverino E, Goeminne PC, McDonnell MJ, Aliberti S, Marshall SE, Loebinger MR, et al. European Respiratory Society guidelines for the management of adult bronchiectasis. Eur Respir J. 2017;50:1700629. - PubMed
-
- Choi H, Yang B, Nam H, Kyoung DS, Sim YS, Park HY, et al. Population-based prevalence of bronchiectasis and associated comorbidities in South Korea. Eur Respir J. 2019;54:1900194. - PubMed
-
- Quittner AL, O’Donnell AE, Salathe MA, Lewis SA, Li X, Montgomery AB, et al. Quality of Life Questionnaire-Bronchiectasis: final psychometric analyses and determination of minimal important difference scores. Thorax. 2015;70:12–20. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

