Clinical repercussions of Glanders (Burkholderia mallei infection) in a Brazilian child: a case report
- PMID: 32578712
- PMCID: PMC7310367
- DOI: 10.1590/0037-8682-0054-2020
Clinical repercussions of Glanders (Burkholderia mallei infection) in a Brazilian child: a case report
Abstract
Glanders is a relatively unknown zoonotic disease caused by Burkholderia mallei. This bacterium affect solipeds and humans, and can be used as a biological warfare. Glanders is characterized as an occupational disease. We report the case of an 11-year-old boy who was presented to an emergency department with chest pain and dyspnea. He evolved into septic shock, pneumonia, and multiple abscesses. B. mallei was found in the exudate culture. Human infection is rare and difficult to confirm. The knowledge on glanders is important for differential diagnosis from other serious illnesses causing pneumonia and multiple abscesses.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
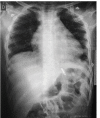
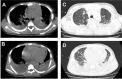
Similar articles
-
Clinical and Molecular Characterization of Human Burkholderia mallei Infection, Brazil.Emerg Infect Dis. 2024 Nov;30(11):2400-2403. doi: 10.3201/eid3011.240549. Emerg Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 39447175 Free PMC article.
-
A Case Report of Burkholderia mallei Infection Leading to Pneumonia.Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2023;26(1):241-245. doi: 10.2174/1386207325666220509152221. Comb Chem High Throughput Screen. 2023. PMID: 35579163
-
A novel selective medium for the isolation of Burkholderia mallei from equine specimens.BMC Vet Res. 2019 May 7;15(1):133. doi: 10.1186/s12917-019-1874-0. BMC Vet Res. 2019. PMID: 31064357 Free PMC article.
-
Glanders in animals: a review on epidemiology, clinical presentation, diagnosis and countermeasures.Transbound Emerg Dis. 2013 Jun;60(3):204-21. doi: 10.1111/j.1865-1682.2012.01342.x. Epub 2012 May 27. Transbound Emerg Dis. 2013. PMID: 22630609 Review.
-
Burkholderia mallei and Burkholderia pseudomallei: the causative micro-organisms of glanders and melioidosis.Recent Pat Antiinfect Drug Discov. 2007 Nov;2(3):233-41. doi: 10.2174/157489107782497335. Recent Pat Antiinfect Drug Discov. 2007. PMID: 18221181 Review.
Cited by
-
Fatal hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis-induced multiorgan dysfunction secondary to Burkholderia pseudomallei sepsis: A case report.World J Clin Cases. 2023 Oct 26;11(30):7372-7379. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v11.i30.7372. World J Clin Cases. 2023. PMID: 37969441 Free PMC article.
-
Glanders (Burkholderia mallei infection) in an Iranian man: A case report.IDCases. 2023 Apr 29;32:e01779. doi: 10.1016/j.idcr.2023.e01779. eCollection 2023. IDCases. 2023. PMID: 37187940 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and Molecular Characterization of Human Burkholderia mallei Infection, Brazil.Emerg Infect Dis. 2024 Nov;30(11):2400-2403. doi: 10.3201/eid3011.240549. Emerg Infect Dis. 2024. PMID: 39447175 Free PMC article.
-
Current and Future Advances in the Detection and Surveillance of Biosecurity-Relevant Equine Bacterial Diseases Using Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification (LAMP).Animals (Basel). 2023 Aug 18;13(16):2663. doi: 10.3390/ani13162663. Animals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37627456 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Patient Presenting with Abscess Unresponsive to Treatment and Progressive to Osteomyelitis: A Rare Cause Burkholderia mallei.Sisli Etfal Hastan Tip Bul. 2024 Jun 28;58(2):258-261. doi: 10.14744/SEMB.2023.70194. eCollection 2024. Sisli Etfal Hastan Tip Bul. 2024. PMID: 39021687 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Whitlock GC, Estes DM, Torres AG. Glanders: off to the races with Burkholderia mallei. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2007;277(2):115–122. - PubMed
-
- Verma AK Saminathan M, Neha Tiwari R, Dhama K Singh SV. Glanders-A Re-emerging Zoonotic Disease: A Review. J Biol Sci. 2014;14(1):38–51.
-
- Georgiades C, Fishman EK. Glanders Disease of the Liver and Spleen: CT Evaluation. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2001;25(1):91–93. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

