Screening of Chloroquine, Hydroxychloroquine and its derivatives for their binding affinity to multiple SARS-CoV-2 protein drug targets
- PMID: 32579059
- PMCID: PMC7332874
- DOI: 10.1080/07391102.2020.1782265
Screening of Chloroquine, Hydroxychloroquine and its derivatives for their binding affinity to multiple SARS-CoV-2 protein drug targets
Abstract
Recently Chloroquine and its derivative Hydroxychloroquine have garnered enormous interest amongst the clinicians and health authorities' world over as a potential treatment to contain COVID-19 pandemic. The present research aims at investigating the therapeutic potential of Chloroquine and its potent derivative Hydroxychloroquine against SARS-CoV-2 viral proteins. At the same time screening was performed for some chemically synthesized derivatives of Chloroquine and compared their binding efficacy with chemically synthesized Chloroquine derivatives through in silico approaches. For the purpose of the study, some essential viral proteins and enzymes were selected that are implicated in SARS-CoV-2 replication and multiplication as putative drug targets. Chloroquine, Hydroxychloroquine, and some of their chemically synthesized derivatives, taken from earlier published studies were selected as drug molecules. We have conducted molecular docking and related studies between Chloroquine and its derivatives and SARS-CoV-2 viral proteins, and the findings show that both Chloroquine and Hydroxychloroquine can bind to specific structural and non-structural proteins implicated in the pathogenesis of SARS-CoV-2 infection with different efficiencies. Our current study also shows that some of the chemically synthesized Chloroquine derivatives can also potentially inhibit various SARS-CoV-2 viral proteins by binding to them and concomitantly effectively disrupting the active site of these proteins. These findings bring into light another possible mechanism of action of Chloroquine and Hydroxychloroquine and also pave the way for further drug repurposing and remodeling.Communicated by Ramaswamy H. Sarma.
Keywords: COVID-19; Chloroquine derivatives; Hydroxychloroquine; SARS-CoV-2; molecular docking.
Figures
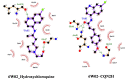
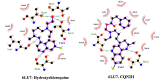
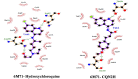
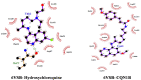
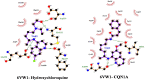
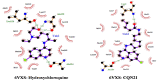
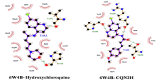
References
-
- Bommu U. D., Konidala K. K., Pamanji R., & Yeguvapalli S. (2019). Structural probing, screening and structure-based drug repositioning insights into the identification of potential Cox-2 inhibitors from selective coxibs. Interdisciplinary Sciences: Computational Life Sciences, 11(2), 153–169. 10.1007/s12539-017-0244-5 - DOI - PubMed
-
- CEBM (2020). Global Covid-19 case fatality rates Retrieved May 7, 2020, from https://www.cebm.net/covid-19/global-covid-19-case-fatality-rates/.
-
- DeLano W. L. (2002). Pymol: An open-source molecular graphics tool. CCP4 Newsletter on Protein Crystallography, 40(1), 82–92.
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
