Mouse brain transcriptome responses to inhaled nanoparticulate matter differed by sex and APOE in Nrf2-Nfkb interactions
- PMID: 32579111
- PMCID: PMC7314548
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.54822
Mouse brain transcriptome responses to inhaled nanoparticulate matter differed by sex and APOE in Nrf2-Nfkb interactions
Abstract
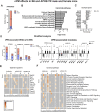
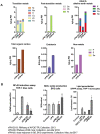
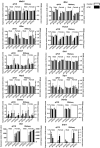
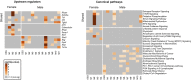
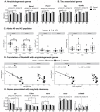
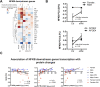
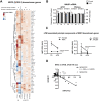
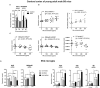
The neurotoxicity of air pollution is undefined for sex and APOE alleles. These major risk factors of Alzheimer's disease (AD) were examined in mice given chronic exposure to nPM, a nano-sized subfraction of urban air pollution. In the cerebral cortex, female mice had two-fold more genes responding to nPM than males. Transcriptomic responses to nPM had sex-APOE interactions in AD-relevant pathways. Only APOE3 mice responded to nPM in genes related to Abeta deposition and clearance (Vav2, Vav3, S1009a). Other responding genes included axonal guidance, inflammation (AMPK, NFKB, APK/JNK signaling), and antioxidant signaling (NRF2, HIF1A). Genes downstream of NFKB and NRF2 responded in opposite directions to nPM. Nrf2 knockdown in microglia augmented NFKB responses to nPM, suggesting a critical role of NRF2 in air pollution neurotoxicity. These findings give a rationale for epidemiologic studies of air pollution to consider sex interactions with APOE alleles and other AD-risk genes.
Keywords: APOE; Nrf2; air pollution; computational biology; mouse; neuroscience; nf-kb; sex; systems biology; transcriptome.
© 2020, Haghani et al.
Conflict of interest statement
AH, MC, KD, CD, MT, NS, ML, CS, TT, HF, HZ, TM, CF No competing interests declared
Figures



References
-
- Cacciottolo M, Wang X, Driscoll I, Woodward N, Saffari A, Reyes J, Serre ML, Vizuete W, Sioutas C, Morgan TE, Gatz M, Chui HC, Shumaker SA, Resnick SM, Espeland MA, Finch CE, Chen JC. Particulate air pollutants, APOE alleles and their contributions to cognitive impairment in older women and to amyloidogenesis in experimental models. Translational Psychiatry. 2017;7:e1022. doi: 10.1038/tp.2016.280. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cacciottolo M, Morgan TE, Saffari AA, Shirmohammadi F, Forman HJ, Sioutas C, Finch CE. Traffic-related air pollutants (TRAP-PM) promote neuronal amyloidogenesis through oxidative damage to lipid rafts. Free Radical Biology and Medicine. 2020;147:242–251. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2019.12.023. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Calderón-Garcidueñas L, Kavanaugh M, Block M, D'Angiulli A, Delgado-Chávez R, Torres-Jardón R, González-Maciel A, Reynoso-Robles R, Osnaya N, Villarreal-Calderon R, Guo R, Hua Z, Zhu H, Perry G, Diaz P. Neuroinflammation, hyperphosphorylated tau, diffuse amyloid plaques, and down-regulation of the cellular prion protein in air pollution exposed children and young adults. Journal of Alzheimer's Disease. 2012;28:93–107. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2011-110722. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
- RF1 AG053982/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 1RF1AG053982-01A1/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005142/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AG000037/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS076794/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG066530/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 4R00AG052604-02/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 1R01AG057912-01/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R00 AG052604/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG051521/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- T32 AG052374/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG055367/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01AG051521/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG057911/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P50AG05142/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG057912/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

