miR-26b-5p/TCF-4 Controls the Adipogenic Differentiation of Human Adipose-derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells
- PMID: 32579400
- PMCID: PMC7563810
- DOI: 10.1177/0963689720934418
miR-26b-5p/TCF-4 Controls the Adipogenic Differentiation of Human Adipose-derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells
Abstract
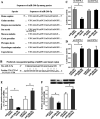
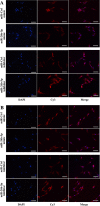
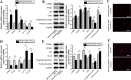
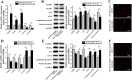
In this study, we assessed the ability of miR-26b-5p to regulate T cell factor 4 (TCF-4) expression and thereby control human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell (hADMSC) adipogenic differentiation. Adipogenic medium was used to induce hADMSC differentiation over a 6-d period. The ability of miR-26b-5p to interact with the TCF-4 mRNA was confirmed through both predictive bioinformatics analyses and luciferase reporter assays. Immunofluorescent staining was used to visualize the impact of miR-26b-5p inhibition or overexpression on TCF-4 and β-catenin levels in hADMSCs. Further functional analyses were conducted by transfecting these cells with siRNAs specific for TCF-4 and β-catenin. Adipogenic marker and Wnt/β-catenin pathway gene expression levels were assessed via real-time polymerase chain reaction and western blotting. β-catenin localization was assessed via immunofluorescent staining. As expected, our adipogenic media induced the adipocytic differentiation of hADMSCs. In addition, we confirmed that TCF-4 is an miR-26b-5p target gene in these cells, and that protein levels of both TCF-4 and β-catenin were reduced when these cells were transfected with miR-26b-5p mimics. Overexpression of this microRNA also enhanced hADMSC adipogenesis, whereas TCF-4 and β-catenin overexpression inhibited this process. The enhanced hADMSC adipogenic differentiation that was observed following TCF-4 or β-catenin knockdown was partially reversed when miR-26b-5p expression was inhibited. We found that miR-26b-5p serves as a direct negative regulator of TCF-4 expression within hADMSCs, leading to inactivation of the Wnt/β-catenin pathway and thereby promoting the adipogenic differentiation of these cells in vitro.
Keywords: TCF-4; Wnt/β-catenin pathway; adipogenic differentiation; hADMSCs; miRNA-26b-5p.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

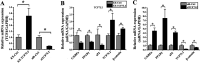
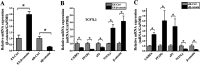
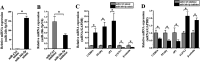
Similar articles
-
miR-204-5p promotes the adipogenic differentiation of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells by modulating DVL3 expression and suppressing Wnt/β-catenin signaling.Int J Mol Med. 2015 Jun;35(6):1587-95. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2015.2160. Epub 2015 Mar 31. Int J Mol Med. 2015. PMID: 25847080 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA HCG11 Inhibits Adipocyte Differentiation in Human Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells by Sponging miR-204-5p to Upregulate SIRT1.Cell Transplant. 2020 Jan-Dec;29:963689720968090. doi: 10.1177/0963689720968090. Cell Transplant. 2020. PMID: 33086891 Free PMC article.
-
Upregulation of miR-22 promotes osteogenic differentiation and inhibits adipogenic differentiation of human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells by repressing HDAC6 protein expression.Stem Cells Dev. 2012 Sep 1;21(13):2531-40. doi: 10.1089/scd.2012.0014. Epub 2012 Apr 2. Stem Cells Dev. 2012. PMID: 22375943 Free PMC article.
-
Adipogenic miRNA and meta-signature miRNAs involved in human adipocyte differentiation and obesity.Oncotarget. 2016 Jun 28;7(26):40830-40845. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.8518. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27049726 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aging and Metabolic Reprogramming of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Affect Molecular Mechanisms Related to Cardiovascular Diseases.Cells. 2023 Dec 7;12(24):2785. doi: 10.3390/cells12242785. Cells. 2023. PMID: 38132104 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
CircPVT1 promotes the tumorigenesis and metastasis of osteosarcoma via mediation of miR-26b-5p/CCNB1 axis.J Bone Miner Metab. 2022 Jul;40(4):581-593. doi: 10.1007/s00774-022-01326-6. Epub 2022 Jun 1. J Bone Miner Metab. 2022. PMID: 35648221
-
Transcription Factor-7-Like-2 (TCF7L2) in Atherosclerosis: A Potential Biomarker and Therapeutic Target.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021 Sep 9;8:701279. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2021.701279. eCollection 2021. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2021. PMID: 34568447 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunomodulatory Properties of Human Breast Milk: MicroRNA Contents and Potential Epigenetic Effects.Biomedicines. 2022 May 24;10(6):1219. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10061219. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35740242 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-26b-5p Targets DAPK1 to Reduce Intestinal Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury via Inhibition of Intestinal Mucosal Cell Apoptosis.Dig Dis Sci. 2022 May;67(5):1794-1805. doi: 10.1007/s10620-021-06975-7. Epub 2021 Apr 10. Dig Dis Sci. 2022. PMID: 33839982 Free PMC article.
-
Programming of postnatal phenotype caused by exposure of cultured embryos from Brahman cattle to colony-stimulating factor 2 and serum.J Anim Sci. 2021 Aug 1;99(8):skab180. doi: 10.1093/jas/skab180. J Anim Sci. 2021. PMID: 34079989 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bradford BD, Lee JW. Reconstruction of the forehead and scalp. Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am. 2019;27(1):85–94. - PubMed
-
- Saban Y. Rhinoplasty: Lessons from “errors”: from anatomy and experience to the concept of sequential primary rhinoplasty. HNO. 2018;66(1):15–25. - PubMed
-
- Stephan S, Reinisch J. Auricular reconstruction using porous polyethylene implant technique. Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am. 2018;26(1):69–85. - PubMed
-
- Denadai R, Raposo-Amaral CA, Raposo-Amaral CE. Fat grafting in managing craniofacial deformities. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2019;143(5):1447–1455. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

