A Phase 3, Multicenter, Randomized, Two-Arm, Open-Label Study of Intermittent Oral Dosing of Roxadustat for the Treatment of Anemia in Japanese Erythropoiesis-Stimulating Agent-Naïve Chronic Kidney Disease Patients Not on Dialysis
- PMID: 32580188
- PMCID: PMC7592955
- DOI: 10.1159/000508100
A Phase 3, Multicenter, Randomized, Two-Arm, Open-Label Study of Intermittent Oral Dosing of Roxadustat for the Treatment of Anemia in Japanese Erythropoiesis-Stimulating Agent-Naïve Chronic Kidney Disease Patients Not on Dialysis
Abstract
Introduction: Roxadustat is an oral hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor approved for the treatment of anemia in Japan for patients with dialysis-dependent (DD) chronic kidney disease (CKD).
Objective: Multicenter, randomized, open-label, noncomparative, phase 3 study to evaluate roxadustat for anemia of non-dialysis-dependent (NDD) CKD in Japan.
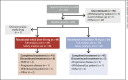
Methods: Erythropoiesis stimulating agent (ESA)-naïve NDD-CKD patients were randomized to roxadustat (initial dose, 50 or 70 mg 3 times weekly), titrated to maintain hemoglobin (Hb) within 10.0-12.0 g/dL, for ≤24 weeks. Patients with either transferrin saturation of ≥5% or serum ferritin of ≥30 ng/mL during the screening period were eligible. Endpoints included response rate (proportion of patients achieving Hb ≥10.0 or ≥10.5 g/dL and Hb increase ≥1.0 g/dL from baseline) at end of treatment; average Hb (weeks 18-24); change of average Hb from baseline to weeks 18-24; maintenance rate (proportion of patients achieving Hb 10.0-12.0 g/dL at weeks 18-24); rate of rise (RoR) of Hb from weeks 0-4, discontinuation, or dose adjustment. Adverse events were monitored throughout the study.
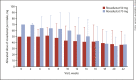
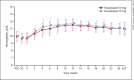
Results: Of 135 patients who provided informed consent, 100 were randomized and 99 received roxadustat (50 mg, n = 49; 70 mg, n = 50). The mean (SD) dose of roxadustat per intake at week 22 was 36.3 (22.7) mg in the roxadustat 50 mg group and 36.8 (16.0) mg in the roxadustat 70 mg group. Prior medications included oral iron therapy (20.2%) and intravenous iron therapy (1.0%). Overall response rate (95% CI) was 97.0% (91.4, 99.4; Hb ≥10.0 g/dL) and 94.9% (88.6, 98.3; Hb ≥10.5 g/dL). Mean (SD) Hb (weeks 18-24) was 11.17 (0.62) g/dL. Mean (SD) change of Hb from baseline (weeks 18-24) was 1.34 (0.86) g/dL. Maintenance rate (95% CI) was 88.8% (80.3, 94.5) among patients with ≥1 Hb measurement during weeks 18-24. Mean (SD) RoR of Hb was 0.291 (0.197) g/dL/week (50 mg) and 0.373 (0.235) g/dL/week (70 mg). Nasopharyngitis and hypertension were the most common adverse events.
Conclusion: Roxadustat increased and maintained Hb in ESA-naïve, partially iron-depleted NDD-CKD patients with anemia.
Keywords: Anemia; Chronic kidney disease; Erythropoiesis-stimulating agent naïve patients; Non-dialysis-dependent patients; Roxadustat.
© 2020 The Author(s) Published by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
Tadao Akizawa reports personal fees from Astellas during the conduct of the study and personal fees from Bayer Yakuhin, Ltd.; Japan Tobacco, Inc.; GlaxoSmithKline; Kissei Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.; Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.; Ono Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.; Fuso Pharmaceutical Industries, Ltd.; Nipro Corporation; Kyowa Kirin; Torii Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.; Sanwa Chemical; and Otsuka outside of the submitted work. Michael Reusch is an employee of Astellas Pharma Europe B.V. Tetsuro Otsuka and Yusuke Yamaguchi are employees of Astellas Pharma, Inc., and Tetsuro Otsuka owns stock at Astellas Pharma, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Fishbane S, Spinowitz B. Update on anemia in ESRD and earlier stages of CKD: core curriculum 2018. Am J Kidney Dis. 2018;71((3)):423–35. - PubMed
-
- Akizawa T, Okumura H, Alexandre AF, Fukushima A, Kiyabu G, Dorey J. Burden of anemia in chronic kidney disease patients in Japan: a literature review. Ther Apher Dial. 2018;22((5)):444–56. - PubMed
-
- Del Vecchio L, Locatelli F. An overview on safety issues related to erythropoiesis-stimulating agents for the treatment of anaemia in patients with chronic kidney disease. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 2016;15((8)):1021–30. - PubMed
-
- Johnson DW, Pollock CA, Macdougall IC. Erythropoiesis-stimulating agent hyporesponsiveness. Nephrology (Carlton) 2007;12((4)):321–30. - PubMed
-
- Locatelli F, Del Vecchio L. Will there still be a role for the originator erythropoiesis-simulating agents after the biosimilars and the hypoxia-inducible factor stabilizers approval? Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2018;27((5)):339–44. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

