Interferon Alpha Induces Multiple Cellular Proteins That Coordinately Suppress Hepadnaviral Covalently Closed Circular DNA Transcription
- PMID: 32581092
- PMCID: PMC7431811
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.00442-20
Interferon Alpha Induces Multiple Cellular Proteins That Coordinately Suppress Hepadnaviral Covalently Closed Circular DNA Transcription
Abstract
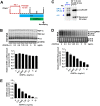
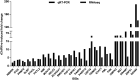
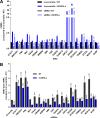
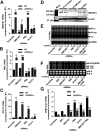
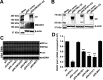
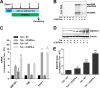
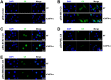
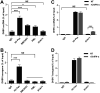
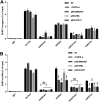
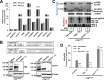
Covalently closed circular DNA (cccDNA) of hepadnaviruses exists as an episomal minichromosome in the nucleus of an infected hepatocyte and serves as the template for the transcription of viral mRNAs. It had been demonstrated by others and us that interferon alpha (IFN-α) treatment of hepatocytes induced a prolonged suppression of human and duck hepatitis B virus cccDNA transcription, which is associated with the reduction of cccDNA-associated histone modifications specifying active transcription (H3K9ac or H3K27ac), but not the histone modifications marking constitutive (H3K9me3) or facultative (H3K27me3) heterochromatin formation. In our efforts to identify IFN-induced cellular proteins that mediate the suppression of cccDNA transcription by the cytokine, we found that downregulating the expression of signal transducer and activator of transcription 1 (STAT1), structural maintenance of chromosomes flexible hinge domain containing 1 (SMCHD1), or promyelocytic leukemia (PML) protein increased basal level of cccDNA transcription activity and partially attenuated IFN-α suppression of cccDNA transcription. In contrast, ectopic expression of STAT1, SMCHD1, or PML significantly reduced cccDNA transcription activity. SMCHD1 is a noncanonical SMC family protein and implicated in epigenetic silencing of gene expression. PML is a component of nuclear domain 10 (ND10) and is involved in suppressing the replication of many DNA viruses. Mechanistic analyses demonstrated that STAT1, SMCHD1, and PML were recruited to cccDNA minichromosomes and phenocopied the IFN-α-induced posttranslational modifications of cccDNA-associated histones. We thus conclude that STAT1, SMCHD1, and PML may partly mediate the suppressive effect of IFN-α on hepadnaviral cccDNA transcription.IMPORTANCE Pegylated IFN-α is the only therapeutic regimen that can induce a functional cure of chronic hepatitis B in a small, but significant, fraction of treated patients. Understanding the mechanisms underlying the antiviral functions of IFN-α in hepadnaviral infection may reveal molecular targets for development of novel antiviral agents to improve the therapeutic efficacy of IFN-α. By a loss-of-function genetic screening of individual IFN-stimulated genes (ISGs) on hepadnaviral mRNAs transcribed from cccDNA, we found that downregulating the expression of STAT1, SMCHD1, or PML significantly increased the level of viral RNAs without altering the level of cccDNA. Mechanistic analyses indicated that those cellular proteins are recruited to cccDNA minichromosomes and induce the posttranslational modifications of cccDNA-associated histones similar to those induced by IFN-α treatment. We have thus identified three IFN-α-induced cellular proteins that suppress cccDNA transcription and may partly mediate IFN-α silencing of hepadnaviral cccDNA transcription.
Keywords: cccDNA; hepatitis B virus; interferons; transcription.
Copyright © 2020 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Intracellular interferon signalling pathways as potential regulators of covalently closed circular DNA in the treatment of chronic hepatitis B.World J Gastroenterol. 2021 Apr 14;27(14):1369-1391. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i14.1369. World J Gastroenterol. 2021. PMID: 33911462 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Alpha-interferon suppresses hepadnavirus transcription by altering epigenetic modification of cccDNA minichromosomes.PLoS Pathog. 2013 Sep;9(9):e1003613. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003613. Epub 2013 Sep 12. PLoS Pathog. 2013. PMID: 24068929 Free PMC article.
-
Forkhead O Transcription Factor 4 Restricts HBV Covalently Closed Circular DNA Transcription and HBV Replication through Genetic Downregulation of Hepatocyte Nuclear Factor 4 Alpha and Epigenetic Suppression of Covalently Closed Circular DNA via Interacting with Promyelocytic Leukemia Protein.J Virol. 2022 Jul 13;96(13):e0054622. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00546-22. Epub 2022 Jun 13. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 35695580 Free PMC article.
-
Interferon-inducible MX2 is a host restriction factor of hepatitis B virus replication.J Hepatol. 2020 May;72(5):865-876. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.12.009. Epub 2019 Dec 18. J Hepatol. 2020. PMID: 31863794
-
Control of cccDNA function in hepatitis B virus infection.J Hepatol. 2009 Sep;51(3):581-92. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2009.05.022. Epub 2009 Jun 10. J Hepatol. 2009. PMID: 19616338 Review.
Cited by
-
Intracellular interferon signalling pathways as potential regulators of covalently closed circular DNA in the treatment of chronic hepatitis B.World J Gastroenterol. 2021 Apr 14;27(14):1369-1391. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i14.1369. World J Gastroenterol. 2021. PMID: 33911462 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Ideal Hallmark Closest to Complete Cure of Chronic Hepatitis B Patients: High-sensitivity Quantitative HBsAg Loss.J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2023 Feb 28;11(1):197-206. doi: 10.14218/JCTH.2022.00289. Epub 2022 Aug 22. J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2023. PMID: 36406318 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chronic Hepatitis B Virus Persistence: Mechanisms and Insights.Cureus. 2025 Feb 13;17(2):e78944. doi: 10.7759/cureus.78944. eCollection 2025 Feb. Cureus. 2025. PMID: 40092015 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An allosteric inhibitor of sirtuin 2 blocks hepatitis B virus covalently closed circular DNA establishment and its transcriptional activity.Antiviral Res. 2024 Jun;226:105888. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2024.105888. Epub 2024 Apr 18. Antiviral Res. 2024. PMID: 38641024 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic drugs against human DNA viruses and retroviruses.Antiviral Res. 2025 Aug;240:106218. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2025.106218. Epub 2025 Jun 23. Antiviral Res. 2025. PMID: 40562219 Review.
References
-
- Alter H, Block T, Brown N, Brownstein A, Brosgart C, Chang KM, Chen PJ, Chisari FV, Cohen C, El-Serag H, Feld J, Gish R, Glenn J, Greten T, Guo H, Guo JT, Hoshida Y, Hu J, Kowdley KV, Li W, Liang J, Locarnini S, Lok AS, Mason W, McMahon B, Mehta A, Perrillo R, Revill P, Rice CM, Rinaudo J, Schinazi R, Seeger C, Shetty K, Tavis J, Zoulim F. 2018. A research agenda for curing chronic hepatitis B virus infection. Hepatology 67:1127–1131. doi:10.1002/hep.29509. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

