A Genetic Risk Score to Personalize Prostate Cancer Screening, Applied to Population Data
- PMID: 32581112
- PMCID: PMC7483627
- DOI: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-19-1527
A Genetic Risk Score to Personalize Prostate Cancer Screening, Applied to Population Data
Abstract
Background: A polygenic hazard score (PHS), the weighted sum of 54 SNP genotypes, was previously validated for association with clinically significant prostate cancer and for improved prostate cancer screening accuracy. Here, we assess the potential impact of PHS-informed screening.
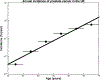
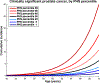
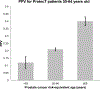
Methods: United Kingdom population incidence data (Cancer Research United Kingdom) and data from the Cluster Randomized Trial of PSA Testing for Prostate Cancer were combined to estimate age-specific clinically significant prostate cancer incidence (Gleason score ≥7, stage T3-T4, PSA ≥10, or nodal/distant metastases). Using HRs estimated from the ProtecT prostate cancer trial, age-specific incidence rates were calculated for various PHS risk percentiles. Risk-equivalent age, when someone with a given PHS percentile has prostate cancer risk equivalent to an average 50-year-old man (50-year-standard risk), was derived from PHS and incidence data. Positive predictive value (PPV) of PSA testing for clinically significant prostate cancer was calculated using PHS-adjusted age groups.
Results: The expected age at diagnosis of clinically significant prostate cancer differs by 19 years between the 1st and 99th PHS percentiles: men with PHS in the 1st and 99th percentiles reach the 50-year-standard risk level at ages 60 and 41, respectively. PPV of PSA was higher for men with higher PHS-adjusted age.
Conclusions: PHS provides individualized estimates of risk-equivalent age for clinically significant prostate cancer. Screening initiation could be adjusted by a man's PHS.
Impact: Personalized genetic risk assessments could inform prostate cancer screening decisions.
©2020 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest
All authors declare no support from any organization for the submitted work except as follows:
A.M. Dale and T.M. Seibert report a research grant from the US Department of Defense. O.A. Andreassen reports research grants from KG Jebsen Stiftelsen, Research Council of Norway, and South East Norway Health Authority.
Authors declare no financial relationships with any organizations that might have an interest in the submitted work in the previous three years except as follows, with all of these relationships outside the present study:
T.M. Seibert reports honoraria from Multimodal Imaging Services Corporation for imaging segmentation, honoraria from WebMD, Inc. for educational content, as well as a past research grant from Varian Medical Systems. A.S. Kibel reports advisory board memberships for Sanofi-Aventis, Dendreon, and Profound. O.A. Andreassen reports speaker honoraria from Lundbeck.
Authors declare no other relationships or activities that could appear to have influenced the submitted work except as follows:
O.A. Andreassen has a patent application # U.S. 20150356243 pending; A.M. Dale also applied for this patent application and assigned it to UC San Diego. A.M. Dale has additional disclosures outside the present work: founder, equity holder, and advisory board member for CorTechs Labs, Inc.; founder and equity holder in HealthLytix, Inc., advisory board member of Human Longevity, Inc.; recipient of nonfinancial research support from General Electric Healthcare. O.A. Andreassen is a consultant for HealthLytix, Inc.
Additional acknowledgments for the PRACTICAL consortium and contributing studies are described in the Supplemental Material.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- L30 CA231417/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 29017/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- K08 EB026503/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- 15064/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 24432/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- P20 GM121288/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- 10118/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 29019/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- P30 CA023100/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 16563/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- 19170/CRUK_/Cancer Research UK/United Kingdom
- R21 CA202417/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

