Identification of Target Genes and Transcription Factors in Mice with LMNA-Related Dilated Cardiomyopathy by Integrated Bioinformatic Analyses
- PMID: 32581210
- PMCID: PMC7313426
- DOI: 10.12659/MSM.924576
Identification of Target Genes and Transcription Factors in Mice with LMNA-Related Dilated Cardiomyopathy by Integrated Bioinformatic Analyses
Abstract
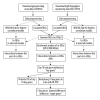
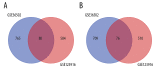
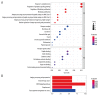
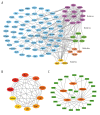
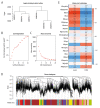
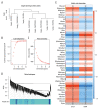
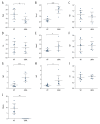
BACKGROUND Dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM), which is characterized by enlarged ventricular dimensions and systolic dysfunction, is the most common type of cardiomyopathy. Mutations in the LMNA gene are reported in approximately 10% of familial DCM cases. However, the mechanism of LMNA mutations in human DCM remains unclear. MATERIAL AND METHODS We used the GSE36502 and GSE123916 datasets to obtain gene expression profiles from LMNA-related DCM mice and to identify differentially expressed genes (DEGs). Crucial function and pathway enrichment analyses of DEGs were performed. Protein-protein interaction (PPI) network analysis was carried out to identify the top 10 hub genes, which were validated using reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) to find target genes. Weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA) was used to explore the module relevant to external traits of LMNA-related DCM mice. Transcription factors (TFs) for the selected genes were analyzed using NetworkAnalyst. RESULTS A total of 156 common DEGs (co-DEGs) were identified, including 80 up-regulated and 76 down-regulated genes. The enriched biological functions and pathways were oxidative stress, regulation of apoptosis, regulation of fibrosis, and MAPK pathways. Five target genes (Timp1, Hmox1, Spp1, Atf3, and Adipoq) were verified after RT-PCR. Most co-DEGs were discovered to be related to the development of external traits. Three TFs (ELF1, ETS1, and NRF1) showed close interactions with the hub genes. CONCLUSIONS Our study used integrated bioinformatic analyses and revealed some important genes in mice with LMNA-related DCM, which could provide novel insights into the mechanism underlying human LMNA-related DCM.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures

References
-
- Hershberger RE, Morales A. LMNA-related dilated cardiomyopathy. In: Adam MP, Ardinger HH, Pagon RA, et al., editors. GeneReviews®. Seattle (WA): University of Washington, Seattle; 1993. - PubMed
-
- Weintraub RG, Semsarian C, Macdonald P. Dilated cardiomyopathy. Lancet. 2017;390:400–14. - PubMed
-
- Arbustini E, Pilotto A, Repetto A, et al. Autosomal dominant dilated cardiomyopathy with atrioventricular block: A lamin A/C defect-related disease. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2002;39:981–90. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

