Chronic circadian disruption modulates breast cancer stemness and immune microenvironment to drive metastasis in mice
- PMID: 32581213
- PMCID: PMC7314789
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-020-16890-6
Chronic circadian disruption modulates breast cancer stemness and immune microenvironment to drive metastasis in mice
Abstract
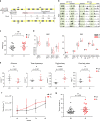
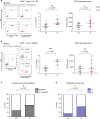
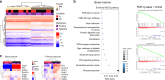
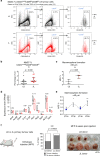
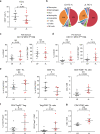
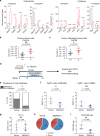
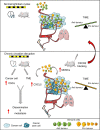
Breast cancer is the most common type of cancer worldwide and one of the major causes of cancer death in women. Epidemiological studies have established a link between night-shift work and increased cancer risk, suggesting that circadian disruption may play a role in carcinogenesis. Here, we aim to shed light on the effect of chronic jetlag (JL) on mammary tumour development. To do this, we use a mouse model of spontaneous mammary tumourigenesis and subject it to chronic circadian disruption. We observe that circadian disruption significantly increases cancer-cell dissemination and lung metastasis. It also enhances the stemness and tumour-initiating potential of tumour cells and creates an immunosuppressive shift in the tumour microenvironment. Finally, our results suggest that the use of a CXCR2 inhibitor could correct the effect of JL on cancer-cell dissemination and metastasis. Altogether, our data provide a conceptual framework to better understand and manage the effects of chronic circadian disruption on breast cancer progression.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Bray F, et al. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. Ca. Cancer J. Clin. 2018;68:394–424. - PubMed
-
- Schernhammer ES, et al. Rotating night shifts and risk of breast cancer in women participating in the nurses’ health study. JNCI J. Natl Cancer Inst. 2001;93:1563–1568. - PubMed
-
- Hansen J. Night shift work and risk of breast cancer. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2017;4:325–339. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

