Shelterin Complex at Telomeres: Implications in Ageing
- PMID: 32581523
- PMCID: PMC7276337
- DOI: 10.2147/CIA.S256425
Shelterin Complex at Telomeres: Implications in Ageing
Abstract
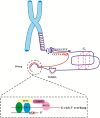
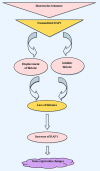
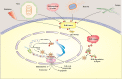
Different factors influence the development and control of ageing. It is well known that progressive telomere shorting is one of the molecular mechanisms underlying ageing. The shelterin complex consists of six telomere-specific proteins which are involved in the protection of chromosome ends. More particularly, this vital complex protects the telomeres from degradation, prevents from activation of unwanted repair systems, regulates the activity of telomerase, and has a crucial role in cellular senescent and ageing-related pathologies. This review explores the organization and function of telomeric DNA along with the mechanism of telomeres during ageing, followed by a discussion of the critical role of shelterin components and their changes during ageing.
Keywords: ageing; sheltering complex; telomeres.
© 2020 Mir et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report that there are no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

