Methyltransferase 3 Mediated miRNA m6A Methylation Promotes Stress Granule Formation in the Early Stage of Acute Ischemic Stroke
- PMID: 32581712
- PMCID: PMC7289951
- DOI: 10.3389/fnmol.2020.00103
Methyltransferase 3 Mediated miRNA m6A Methylation Promotes Stress Granule Formation in the Early Stage of Acute Ischemic Stroke
Abstract
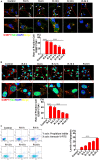
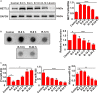
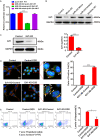
The modification of methyltransferase-like (METTL) enzymes plays important roles in various cellular responses by regulating microRNA expression. However, how m6A modification is involved in stress granule (SG) formation in the early stage of acute ischemic stroke by affecting the biogenesis processing of microRNAs remains unclear. Here, we established a middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO) model in rats and an oxygen-glucose deprivation/reperfusion (OGD/R) model in primary cortical neurons and PC12 cells to explore the potential mechanism between m6A modification and SG formation. The in vivo results showed that the level of infarction and apoptosis increased while SG formation decreased significantly within the ischemic cortex with improved reperfusion time after 2 h of ischemia. Consistent with the in vivo data, an inverse association between the apoptosis level and SG formation was observed in PC12 cells during the reperfusion period after 6 h of OGD stimulation. Both in vivo and in vitro results showed that the expression of METTL3 protein, m6A and miR-335 was significantly decreased with the reperfusion period. Overexpression of the METTL3 and METTL3 gene-knockdown in PC12 cells were achieved via plasmid transfection and CRISPR-Cas9 technology, respectively. Overexpression or knockdown of METTL3 in oxygen-glucose deprivation of PC12 cells resulted in functional maturation of miR-335, SG formation and apoptosis levels. In addition, we found that miR-335 enhanced SG formation through degradation of the mRNA of the eukaryotic translation termination factor (Erf1). In conclusion, we found that METTL3-mediated m6A methylation increases the maturation of miR-335, which promotes SG formation and reduces the apoptosis level of injury neurons and cells, and provides a potential therapeutic strategy for AIS.
Keywords: Erf1; METTL3; acute ischemic stroke; miR-335; stress granules.
Copyright © 2020 Si, Li, Ye, Li, Liu, Kuang, Chen and Zhu.
Figures



Similar articles
-
RNA Binding Protein Motif 3 Inhibits Oxygen-Glucose Deprivation/Reoxygenation-Induced Apoptosis Through Promoting Stress Granules Formation in PC12 Cells and Rat Primary Cortical Neurons.Front Cell Neurosci. 2020 Sep 2;14:559384. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2020.559384. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 32982696 Free PMC article.
-
METTL3 Mediates Microglial Activation and Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability in Cerebral Ischemic Stroke by Regulating NLRP3 Inflammasomes Through m6A Methylation Modification.Neurotox Res. 2024 Feb 13;42(1):15. doi: 10.1007/s12640-024-00687-2. Neurotox Res. 2024. PMID: 38349604
-
METTL3-dependent N6-methyladenosine modification is involved in berberine-mediated neuroprotection in ischemic stroke by enhancing the stability of NEAT1 in astrocytes.Aging (Albany NY). 2024 Jan 4;16(1):299-321. doi: 10.18632/aging.205369. Epub 2024 Jan 4. Aging (Albany NY). 2024. PMID: 38180752 Free PMC article.
-
METTL3-deficiency Suppresses Neural Apoptosis to Induce Protective Effects in Cerebral I/R Injury via Inhibiting RNA m6A Modifications: A Pre-clinical and Pilot Study.Neurochem Res. 2024 Jan;49(1):85-98. doi: 10.1007/s11064-023-04015-6. Epub 2023 Aug 23. Neurochem Res. 2024. PMID: 37610605
-
METTL3 plays multiple functions in biological processes.Am J Cancer Res. 2020 Jun 1;10(6):1631-1646. eCollection 2020. Am J Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 32642280 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
METTL3 promotes microglial inflammation via MEF2C in spinal cord injury.Cell Tissue Res. 2024 Feb;395(2):189-197. doi: 10.1007/s00441-023-03855-6. Epub 2024 Jan 5. Cell Tissue Res. 2024. PMID: 38180567
-
Transcriptome-Wide N6-Methyladenosine Methylome Alteration in the Rat Spinal Cord After Acute Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury.Front Neurosci. 2022 May 30;16:848119. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2022.848119. eCollection 2022. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35706691 Free PMC article.
-
TMAO Promotes NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation of Microglia Aggravating Neurological Injury in Ischemic Stroke Through FTO/IGF2BP2.J Inflamm Res. 2023 Aug 28;16:3699-3714. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S399480. eCollection 2023. J Inflamm Res. 2023. PMID: 37663757 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of m6A methylation-related genes in cerebral ischaemia‒reperfusion of Breviscapus therapy based on bioinformatics methods.BMC Med Genomics. 2023 Sep 5;16(1):210. doi: 10.1186/s12920-023-01651-3. BMC Med Genomics. 2023. PMID: 37670341 Free PMC article.
-
METTL3 Deficiency Aggravates Hepatic Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Mice by Activating the MAPK Signaling Pathway.Int J Med Sci. 2024 Apr 15;21(6):1037-1048. doi: 10.7150/ijms.94177. eCollection 2024. Int J Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 38774758 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

