Berberine Mediated Positive Inotropic Effects on Rat Hearts via a Ca2+-Dependent Mechanism
- PMID: 32581792
- PMCID: PMC7289965
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00821
Berberine Mediated Positive Inotropic Effects on Rat Hearts via a Ca2+-Dependent Mechanism
Abstract
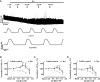
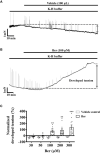
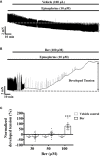
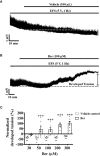
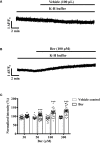
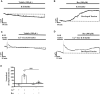
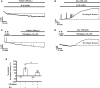
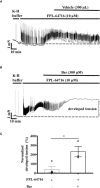
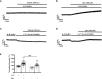
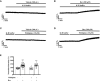
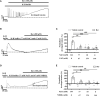
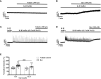
Previous studies showed that berberine, an alkaloid from Coptis Chinensis Franch, might exert a positive inotropic effect on the heart. However, the underlying mechanisms were unclear. Here, we reported that berberine at 10-20 µM increased the left ventricular (LV) developed pressure and the maximal rate of the pressure rising, and it increased the maximal rate of the pressure descending at 20 µM in Langendorff-perfused isolated rat hearts. These effects diminished with the concentration of berberine increasing to 50 µM. In the concentration range of 50-300 µM, berberine increased the isometric tension of isolated left ventricular muscle (LVM) strips with or without electrical stimulations, and it (30-300 µM) also increased the intracellular Ca2+ level in the isolated LV myocytes. The removal of extracellular Ca2+ hindered the berberine-induced increases in the tension of LVM strips and the intracellular Ca2+ level of LV myocytes. These suggested that berberine might exert its positive inotropic effects via enhancing Ca2+ influx. The blockade of L-type Ca2+ channels (LTCCs) with nifedipine significantly attenuated 300 μM berberine-induced tension increase in LVM strips but not the increase in the intracellular Ca2+ level. Berberine (300 μM) further increased the LVM tension following the treatment with the LTCC opener FPL-64716 (10 μM), indicating an LTCC-independent effect of berberine. Lowering extracellular Na+ attenuated the berberine-induced increases in both the tension of LVM strips and the intracellular Ca2+ level of LV myocytes. In conclusion, berberine might exert a positive inotropic effect on the isolated rat heart by enhancing the Ca2+ influx in LV myocytes; these were extracellular Na+-dependent.
Keywords: Ca2+; Na+; berberine; heart; positive inotropic effect.
Copyright © 2020 Zhao, Wang, Gao, Jing and Xin.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

