Targeting Calcium Homeostasis in Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury: An Overview of Regulatory Mechanisms and Therapeutic Reagents
- PMID: 32581817
- PMCID: PMC7296066
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2020.00872
Targeting Calcium Homeostasis in Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury: An Overview of Regulatory Mechanisms and Therapeutic Reagents
Abstract
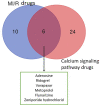
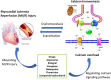
Calcium homeostasis plays an essential role in maintaining excitation-contraction coupling (ECC) in cardiomyocytes, including calcium release, recapture, and storage. Disruption of calcium homeostasis may affect heart function, leading to the development of various heart diseases. Myocardial ischemia/reperfusion (MI/R) injury may occur after revascularization, which is a treatment used in coronary heart disease. MI/R injury is a complex pathological process, and the main cause of increased mortality and disability after treatment of coronary heart disease. However, current methods and drugs for treating MI/R injury are very scarce, not ideal, and have limitations. Studies have shown that MI/R injury can cause calcium overload that can further aggravate MI/R injury. Therefore, we reviewed the effects of critical calcium pathway regulators on MI/R injury and drew an intuitive diagram of the calcium homeostasis pathway. We also summarized and analyzed calcium pathway-related or MI/R drugs under research or marketing by searching Therapeutic Target and PubMed Databases. The data analysis showed that six drugs and corresponding targets are used to treat MI/R injury and involved in calcium signaling pathways. We emphasize the relevance of further detailed investigation of MI/R injury and calcium homeostasis and the therapeutic role of calcium homeostasis in MI/R injury, which bridges basic research and clinical applications of MI/R injury.
Keywords: Therapeutic Target Database; calcium homeostasis; calcium signaling pathway; myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury; therapeutic reagents.
Copyright © 2020 Wang, Wang, He, Sun and Sun.
Figures
References
-
- Åström-Olsson K., Karlsson L., Mattsson Hultén L., Davidsson P., Mantovani V., Månsson C., et al. (2009). Myocardial release of FKBP12 and increased production of FKBP12.6 in ischemia and reperfusion experimental models. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 390, 1299–1304. 10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.10.140 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

