Mechanisms Associated to Nitroxyl (HNO)-Induced Relaxation in the Intestinal Smooth Muscle
- PMID: 32581821
- PMCID: PMC7283591
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00438
Mechanisms Associated to Nitroxyl (HNO)-Induced Relaxation in the Intestinal Smooth Muscle
Abstract
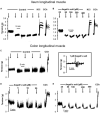
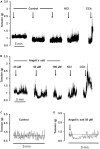
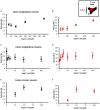
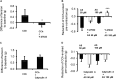
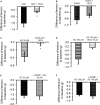
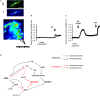
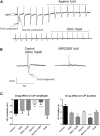
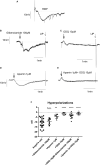
The pharmacological properties of nitroxyl (HNO) donors in the gastrointestinal tract are unknown. We investigated the properties of this molecule in the regulation of gastrointestinal contractility focusing on its possible interaction with other gaseous signaling molecules such as NO and H2S. Organ bath, Ca2+ imaging, and microelectrode recordings were performed on rat intestinal samples, using Angeli's salt as HNO donor. Angeli's salt caused a concentration-dependent relaxation of longitudinal or circular muscle strips of the ileum and the proximal colon. This relaxation was strongly inhibited by the Rho-kinase inhibitor Y-27632 (10 μM), by the reducing agent DTT or by the inhibitor of soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC) ODQ (10 μM) alone or in combination with the inhibitors of the endogenous synthesis of H2S β-cyano-L-alanine (5 mM) and amino-oxyacetate (5 mM). Preventing endogenous synthesis of NO by the NO synthase inhibitor L-NAME (200 μM) did not affect the relaxation induced by HNO. HNO induced an increase in cytosolic Ca2+ concentration in colonic myocytes. It also elicited myocyte membrane hyperpolarization that amounted to -10.6 ± 1.1 mV. ODQ (10 μM) and Apamin (1 μM), a selective inhibitor of small conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channels (SKca), strongly antagonized this effect. We conclude that HNO relaxes the gastrointestinal tract musculature by hyperpolarizing myocytes via activation of the sGC/cGMP pathway similarly to NO, not only inhibiting the RhoK and activating MLCP as do both NO and H2S but also increasing cytosolic Ca2+ for activation of SK C a contributing to hyperpolarization.
Keywords: Ca2+; gasotransmitter; membrane potential; motility; nitroxyl (HNO); small conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channels (SKca); soluble guanylate cyclase.
Copyright © 2020 Gastreich-Seelig, Jimenez and Pouokam.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The concomitant coronary vasodilator and positive inotropic actions of the nitroxyl donor Angeli's salt in the intact rat heart: contribution of soluble guanylyl cyclase-dependent and -independent mechanisms.Br J Pharmacol. 2014 Apr;171(7):1722-34. doi: 10.1111/bph.12568. Br J Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24372173 Free PMC article.
-
Actions of Angeli's salt, a nitroxyl (HNO) donor, on ion transport across mucosa-submucosa preparations from rat distal colon.Eur J Pharmacol. 2013 Sep 5;715(1-3):133-41. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.05.031. Epub 2013 Jun 4. Eur J Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23747594
-
Complementary mechanisms of modulation of spontaneous phasic contractions by the gaseous signalling molecules NO, H2S, HNO and the polysulfide Na2S3 in the rat colon.J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 2021 Oct 8;34(4):495-507. doi: 10.1515/jbcpp-2021-0181. eCollection 2023 Jul 1. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34624185
-
Effects of the gaseous signalling molecule nitroxyl (HNO) on myenteric neurons governing intestinal motility.J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 2022 Dec 2;34(5):683-687. doi: 10.1515/jbcpp-2022-0233. eCollection 2023 Sep 1. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36455291
-
The nitroxyl anion (HNO) is a potent dilator of rat coronary vasculature.Cardiovasc Res. 2007 Feb 1;73(3):587-96. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2006.11.018. Epub 2006 Nov 18. Cardiovasc Res. 2007. PMID: 17189622
Cited by
-
Nitroxyl Delivered by Angeli's Salt Causes Short-Lasting Activation Followed by Long-Lasting Deactivation of Meningeal Afferents in Models of Headache Generation.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 19;23(4):2330. doi: 10.3390/ijms23042330. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35216445 Free PMC article.
-
Contractility of isolated colonic smooth muscle strips from rats treated with cancer chemotherapy: differential effects of cisplatin and vincristine.Front Neurosci. 2023 Dec 18;17:1304609. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1304609. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 38192512 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bolz S. S., Vogel L., Sollinger D., Derwand R., de Wit C., Loirand G., et al. (2003). Nitric oxide-induced decrease in calcium sensitivity of resistance arteries is attributable to activation of the myosin light chain phosphatase and antagonized by the RhoA/Rho kinase pathway. Circulation 107 3081–3087. 10.1161/01.Cir.0000074202.19612.8c - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

