Critical Roles of ELVOL4 and IL-33 in the Progression of Obesity-Related Cardiomyopathy via Integrated Bioinformatics Analysis
- PMID: 32581837
- PMCID: PMC7291781
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00542
Critical Roles of ELVOL4 and IL-33 in the Progression of Obesity-Related Cardiomyopathy via Integrated Bioinformatics Analysis
Abstract
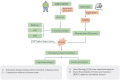
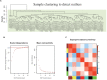
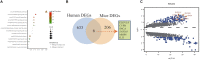
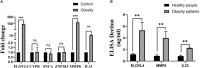
The molecular mechanisms underlying obesity-related cardiomyopathy (ORCM) progression involve multiple signaling pathways, and the pharmacological treatment for ORCM is still limited. Thus, it is necessary to explore new targets and develop novel therapies. Microarray analysis for gene expression profiles using different bioinformatics tools has been an effective strategy for identifying novel targets for various diseases. In this study, we aimed to explore the potential genes related to ORCM using the integrated bioinformatics analysis. The GSE18897 (whole blood expression profiling of obese diet-sensitive, obese diet-resistant, and lean human subjects) and GSE47022 (regular weight C57BL/6 and diet-induced obese C57BL/6 mice) were used for bioinformatics analysis. Weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA) of GSE18897 was employed to investigate gene modules that were strongly correlated with clinical phenotypes. Gene Ontology (GO) functional enrichment analysis and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway analysis were performed on the co-expression genes. The expression levels of the hub genes were validated in the clinical samples. Yellow co-expression module of WGCNA in GSE18897 was found to be significantly related to the caloric restriction treatment. In addition, GO functional enrichment analysis and KEGG pathway analysis were performed on the co-expression genes in yellow co-expression module, which showed an association with oxygen transport and the porphyrins pathway. Overlap analysis of yellow co-expression module genes from GSE18897 andGSE47022 revealed six upregulated genes, and further experimental validation results showed that elongation of very-long-chain fatty acids protein 4 (ELOVL4), matrix metalloproteinase-8 (MMP-8), and interleukin-33 (IL-33) were upregulated in the peripheral blood from patients with ORCM compared to that in the controls. The bioinformatics analysis revealed that ELOVL4 expression levels are positively correlated with that of IL-33. Collectively, using WGCNA in combination with integrated bioinformatics analysis, the hub genes of ELVOL4 and IL-33 might serve as potential biomarkers for diagnosis and/or therapeutic targets for ORCM. The detailed roles of ELVOL4 and IL-33 in the pathophysiology of ORCM still require further investigation.
Keywords: ELOVL4; IL-33; ORCM; WGCNA; yellow co-expression module.
Copyright © 2020 Tao, Wang, Li, Zheng and Liang.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Potentially Critical Roles of NDUFB5, TIMMDC1, and VDAC3 in the Progression of Septic Cardiomyopathy Through Integrated Bioinformatics Analysis.DNA Cell Biol. 2020 Jan;39(1):105-117. doi: 10.1089/dna.2019.4859. Epub 2019 Nov 27. DNA Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 31794266
-
Identification of biomarkers correlated with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy with co-expression analysis.J Cell Physiol. 2019 Dec;234(12):21999-22008. doi: 10.1002/jcp.28762. Epub 2019 May 6. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 31059139
-
Identifying RBM47, HCK, CD53, TYROBP, and HAVCR2 as Hub Genes in Advanced Atherosclerotic Plaques by Network-Based Analysis and Validation.Front Genet. 2021 Jan 15;11:602908. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2020.602908. eCollection 2020. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 33519905 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of candidate genes associated with papillary thyroid carcinoma pathogenesis and progression by weighted gene co-expression network analysis.Transl Cancer Res. 2021 Feb;10(2):694-713. doi: 10.21037/tcr-20-2866. Transl Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 35116402 Free PMC article.
-
The identification of key genes and pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma by bioinformatics analysis of high-throughput data.Med Oncol. 2017 Jun;34(6):101. doi: 10.1007/s12032-017-0963-9. Epub 2017 Apr 21. Med Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28432618 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol in Young Nondiabetic Coronary Heart Disease Patients.Cardiol Res Pract. 2021 Jul 13;2021:2970568. doi: 10.1155/2021/2970568. eCollection 2021. Cardiol Res Pract. 2021. Retraction in: Cardiol Res Pract. 2023 Oct 11;2023:9796524. doi: 10.1155/2023/9796524. PMID: 34336270 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Potential Inflammatory Mediators in Pericardial Fluids of Patients With Coronary Artery Diseases and Their Association With Plasma Biomarkers.J Cell Mol Med. 2025 Jun;29(11):e70625. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.70625. J Cell Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40437664 Free PMC article.
-
Connections for Matters of the Heart: Network Medicine in Cardiovascular Diseases.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 May 19;9:873582. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.873582. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 35665246 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Decreased Spp1 Expression in Acute Myocardial Infarction after Ischemia and Reperfusion Injury.Cardiol Res Pract. 2021 Aug 13;2021:3925136. doi: 10.1155/2021/3925136. eCollection 2021. Cardiol Res Pract. 2021. Retraction in: Cardiol Res Pract. 2023 Oct 11;2023:9870810. doi: 10.1155/2023/9870810. PMID: 34426769 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Identification and validation of potential novel biomarkers to predict distant metastasis in differentiated thyroid cancer.Ann Transl Med. 2021 Jul;9(13):1053. doi: 10.21037/atm-21-383. Ann Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 34422965 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

