Dysregulated Neurovascular Control Underlies Declining Microvascular Functionality in People With Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) at Risk of Liver Fibrosis
- PMID: 32581841
- PMCID: PMC7283580
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00551
Dysregulated Neurovascular Control Underlies Declining Microvascular Functionality in People With Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) at Risk of Liver Fibrosis
Abstract
Background/aims: Increasing evidence shows that non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is associated with dysregulation of microvascular perfusion independently of established cardio-metabolic risk factors. We investigated whether hepatic manifestations of NAFLD such as liver fibrosis and liver fat are associated with microvascular hemodynamics through dysregulation of neurovascular control.
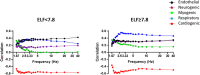
Methods: Microvascular dilator (post-occlusive reactive hyperemia) and sympathetically mediated constrictor (deep inspiratory breath-hold) responses were measured at the forearm and finger, respectively, using laser Doppler fluximetry. Non-linear complexity-based analysis was used to assess the information content and variability of the resting blood flux (BF) signals, attributable to oscillatory flow-motion activity, and over multiple sampling frequencies.
Results: Measurements were made in 189 adults (113 men) with NAFLD, with (n = 65) and without (n = 124) type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), age = 50.9 ± 11.7 years (mean ± SD). Microvascular dilator and constrictor capacity were both negatively associated with age (r = -0.178, p = 0.014, and r = -0.201, p = 0.007, respectively) and enhanced liver fibrosis (ELF) score (r = -0.155, p = 0.038 and r = -0.418, p < 0.0001, respectively). There was no association with measures of liver fat, obesity or T2DM. Lempel-Ziv complexity (LZC) and sample entropy (SE) of the BF signal measured at the two skin sites were associated negatively with age (p < 0.01 and p < 0.001) and positively with ELF score (p < 0.05 and p < 0.0001). In individuals with an ELF score ≥7.8 the influence of both neurogenic and respiratory flow-motion activity on LZC was up-rated (p < 0.0001).
Conclusion: Altered microvascular network functionality occurs in adults with NAFLD suggesting a mechanistic role for dysregulated neurovascular control in individuals at risk of severe liver fibrosis.
Keywords: NAFLD; blood flow; flow-motion; liver fibrosis; microcirculation; non-linear complexity analysis; skin; sympathetic nervous system.
Copyright © 2020 Clough, Chipperfield, Thanaj, Scorletti, Calder and Byrne.
Figures



References
-
- Albano A. M., Brodfuehrer P. D., Cellucci C. J., Tigno X. T., Rapp P. E. (2008). Time series analysis, or the quest for quantitative measures of time dependent behavior. Philip. Sci. Let. 1 18–31.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

