Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Mitigate Palmitate-Induced Impairments in Skeletal Muscle Cell Viability and Differentiation
- PMID: 32581844
- PMCID: PMC7283920
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2020.00563
Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Mitigate Palmitate-Induced Impairments in Skeletal Muscle Cell Viability and Differentiation
Abstract
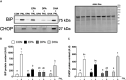
Accumulation of excess saturated free fatty acids such as palmitate (PAL) in skeletal muscle leads to reductions in mitochondrial integrity, cell viability and differentiation. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (n-3 PUFAs) such as eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) counteract PAL-induced lipid accumulation. EPA and DHA, as well as the n-3 PUFA docosapentaenoic acid (DPA), may therefore mitigate PAL-induced lipotoxicity to promote skeletal muscle cell survival and differentiation. C2C12 myoblasts were treated with 50 μM EPA, DPA, or DHA in the absence or presence of 500 μM PAL for 16 h either prior to myoblast analysis or induction of differentiation. Myoblast viability and markers of apoptosis, endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and myotube differentiation capacity were investigated using fluorescence microscopy and immunoblotting. High-resolution respirometry was used to assess mitochondrial function and membrane integrity. PAL induced cell death via apoptosis and increased protein content of ER stress markers BiP and CHOP. EPA, DPA, and DHA co-treatment maintained cell viability, prevented PAL-induced apoptosis and attenuated PAL-induced increases in BiP, whereas only DPA prevented increases in CHOP. PAL subsequently reduced protein content of the differentiation marker myogenin and inhibited myotube formation, and all n-3 PUFAs promoted myotube formation in the presence of PAL. Furthermore, DPA prevented PAL-induced release of cytochrome c and maintained mitochondrial integrity. These findings demonstrate the n-3 PUFAs EPA, DPA and DHA elicit similar protective effects against PAL-induced impairments in muscle cell viability and differentiation. Mechanistically, the protective effects of DPA against PAL lipotoxicity are attributable in part to its ability to maintain mitochondrial respiratory capacity via mitigating PAL-induced loss of mitochondrial membrane integrity.
Keywords: DHA; DPA; EPA; mitochondria; myoblast; myotube; n-3 PUFA; saturated fatty acid.
Copyright © 2020 Tachtsis, Whitfield, Hawley and Hoffman.
Figures





Similar articles
-
N-3PUFA differentially modulate palmitate-induced lipotoxicity through alterations of its metabolism in C2C12 muscle cells.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016 Jan;1861(1):12-20. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2015.10.003. Epub 2015 Oct 22. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016. PMID: 26477381
-
Protective action of n-3 fatty acids on benzo[a]pyrene-induced apoptosis through the plasma membrane remodeling-dependent NHE1 pathway.Chem Biol Interact. 2014 Jan 25;207:41-51. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2013.11.002. Epub 2013 Nov 15. Chem Biol Interact. 2014. PMID: 24246761
-
Eicosapentaenoic acid ameliorates palmitate-induced lipotoxicity via the AMP kinase/dynamin-related protein-1 signaling pathway in differentiated H9c2 myocytes.Exp Cell Res. 2017 Feb 1;351(1):109-120. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2017.01.004. Epub 2017 Jan 11. Exp Cell Res. 2017. PMID: 28088331
-
Long-chain omega-3 fatty acids and the brain: a review of the independent and shared effects of EPA, DPA and DHA.Front Aging Neurosci. 2015 Apr 21;7:52. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2015.00052. eCollection 2015. Front Aging Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25954194 Free PMC article. Review.
-
n-3 Polyunsaturated fatty acids for the management of alcoholic liver disease: A critical review.Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2019;59(sup1):S116-S129. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2018.1544542. Epub 2018 Dec 22. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2019. PMID: 30580553 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluating the Impact of Urolithin A Supplementation on Running Performance, Recovery, and Mitochondrial Biomarkers in Highly Trained Male Distance Runners.Sports Med. 2025 Aug 21. doi: 10.1007/s40279-025-02292-5. Online ahead of print. Sports Med. 2025. PMID: 40839339
-
Palmitic Acid Impairs Myogenesis and Alters Temporal Expression of miR-133a and miR-206 in C2C12 Myoblasts.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 9;22(5):2748. doi: 10.3390/ijms22052748. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33803124 Free PMC article.
-
Leukocyte-type 12/15-lipoxygenase is essential for timely inflammation-resolution and effective tissue regeneration following skeletal muscle injury.Mol Metab. 2025 Aug 5;100:102224. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2025.102224. Online ahead of print. Mol Metab. 2025. PMID: 40769490 Free PMC article.
-
Anthracyclins Increase PUFAs: Potential Implications in ER Stress and Cell Death.Cells. 2021 May 11;10(5):1163. doi: 10.3390/cells10051163. Cells. 2021. PMID: 34064765 Free PMC article.
-
Myristic acid selectively augments β-tubulin levels in C2C12 myotubes via diacylglycerol kinase δ.FEBS Open Bio. 2022 Oct;12(10):1788-1796. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.13466. Epub 2022 Jul 27. FEBS Open Bio. 2022. PMID: 35856166 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

