Clinical Implications of Epigenetic Dysregulation in Perinatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Damage
- PMID: 32582011
- PMCID: PMC7296108
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2020.00483
Clinical Implications of Epigenetic Dysregulation in Perinatal Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Damage
Abstract
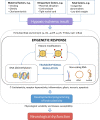
Placental and fetal hypoxia caused by perinatal hypoxic-ischemic events are major causes of stillbirth, neonatal morbidity, and long-term neurological sequelae among surviving neonates. Brain hypoxia and associated pathological processes such as excitotoxicity, apoptosis, necrosis, and inflammation, are associated with lasting disruptions in epigenetic control of gene expression contributing to neurological dysfunction. Recent studies have pointed to DNA (de)methylation, histone modifications, and non-coding RNAs as crucial components of hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy (HIE). The understanding of epigenetic dysregulation in HIE is essential in the development of new clinical interventions for perinatal HIE. Here, we summarize our current understanding of epigenetic mechanisms underlying the molecular pathology of HI brain damage and its clinical implications in terms of new diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic tools.
Keywords: DNA methylation; biomarker; histone modifications; hypoxia; hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy; ischemia; microRNAs.
Copyright © 2020 Bustelo, Barkhuizen, van den Hove, Steinbusch, Bruno, Loidl and Gavilanes.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

