ARP-1 Regulates the Transcriptional Activity of the Aromatase Gene in the Mouse Brain
- PMID: 32582022
- PMCID: PMC7283458
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2020.00306
ARP-1 Regulates the Transcriptional Activity of the Aromatase Gene in the Mouse Brain
Abstract
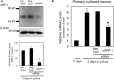
An important function of aromatase in the brain is conversion of testosterone secreted from the testis into estradiol. Estradiol produced in the brain is thought to be deeply involved in the formation of sexually dimorphic nuclei and sexual behavior as a neurosteroid. We analyzed the brain-specific promoter to elucidate the control mechanisms of brain aromatase expression that may be highly involved in sexual differentiation of the brain. The 202-bp upstream region of the brain-specific exon 1 has three types of cis-acting elements, aro-AI, AII, and B. We isolated ARP-1 as an aro-AII-binding protein by yeast one-hybrid screening from a cDNA library of mouse fetal brains. ARP-1 is a member of the nuclear receptor superfamily and functions as an orphan-type transcription factor. ARP-1 protein synthesized in vitro showed the same binding property to the aro-AII site as nuclear extract from fetal brains. To determine how the promoter is involved in brain-specific transcription of the aromatase gene, we first detected the in vivo occupancy of the aro-AII site by ARP-1 using chromatin immunoprecipitation assays. Diencephalic regions of fetal brains at embryonic day 16 were analyzed, which revealed ARP-1 recruitment to the aro-AII site. To analyze the effects of ARP-1 on transcriptional regulation of the brain-specific aromatase promoter, a luciferase reporter plasmid driven by the brain-specific promoter was transfected into CV-1 cells together with a plasmid expressing ARP-1 protein. These analyses revealed that ARP-1 induced promoter activity in a dose-dependent manner. Furthermore, to determine whether ARP-1 is required for aromatase expression in neurons, ARP-1 knockdown was conducted in neuronal cell primary culture. Knockdown of ARP-1 significantly suppressed the increase in aromatase mRNA observed in cultured neurons. These results indicate that ARP-1 is involved in the transcriptional regulation of the brain-specific promoter of the aromatase gene.
Keywords: aromatase; chicken ovalbumin upstream promoter transcription factor; estrogen; nuclear receptor; sexual differentiation; steroid hormone.
Copyright © 2020 Honda and Harada.
Figures




Similar articles
-
LIM-homeodomain transcription factor, Lhx2, is involved in transcriptional control of brain-specific promoter/exon 1f of the mouse aromatase gene.J Neuroendocrinol. 2012 Nov;24(11):1367-74. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2826.2012.02356.x. J Neuroendocrinol. 2012. PMID: 22734700
-
Transcriptional regulation of the nuclear gene encoding the alpha-subunit of the mammalian mitochondrial F1F0 ATP synthase complex: role for the orphan nuclear receptor, COUP-TFII/ARP-1.Biochemistry. 2003 Mar 11;42(9):2656-63. doi: 10.1021/bi0268347. Biochemistry. 2003. PMID: 12614160
-
Stimulation of aromatase P450 promoter (II) activity in endometriosis and its inhibition in endometrium are regulated by competitive binding of steroidogenic factor-1 and chicken ovalbumin upstream promoter transcription factor to the same cis-acting element.Mol Endocrinol. 1999 Feb;13(2):239-53. doi: 10.1210/mend.13.2.0229. Mol Endocrinol. 1999. PMID: 9973254
-
Effects of testosterone and its metabolites on aromatase-immunoreactive cells in the quail brain: relationship with the activation of male reproductive behavior.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1996 Jan;56(1-6 Spec No):185-200. doi: 10.1016/0960-0760(95)00236-7. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1996. PMID: 8603040 Review.
-
Positive and negative transcriptional regulation of aromatase expression in human breast cancer tissue.J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2005 May;95(1-5):17-23. doi: 10.1016/j.jsbmb.2005.04.002. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 2005. PMID: 15955695 Review.
Cited by
-
Brain-derived estrogen and neural function.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2022 Jan;132:793-817. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2021.11.014. Epub 2021 Nov 22. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2022. PMID: 34823913 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuron-Derived Estrogen-A Key Neuromodulator in Synaptic Function and Memory.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 8;22(24):13242. doi: 10.3390/ijms222413242. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34948039 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baulieu EE. Neurosteroids: of the nervous system, by the nervous system, for the nervous system. Recent Prog Horm Res. (1997) 52:1–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

