Interleukin-17 in Chronic Inflammatory Neurological Diseases
- PMID: 32582147
- PMCID: PMC7283538
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00947
Interleukin-17 in Chronic Inflammatory Neurological Diseases
Abstract
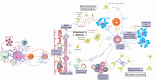
A critical role for IL-17, a cytokine produced by T helper 17 (Th17) cells, has been indicated in the pathogenesis of chronic inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. A positive effect of blockade of IL-17 secreted by autoreactive T cells has been shown in various inflammatory diseases. Several cytokines, whose production is affected by environmental factors, control Th17 differentiation and its maintenance in tissues during chronic inflammation. The roles of IL-17 in the pathogenesis of chronic neuroinflammatory conditions, multiple sclerosis (MS), experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), Alzheimer's disease, and ischemic brain injury are reviewed here. The role of environmental stimuli in Th17 differentiation is also summarized, highlighting the role of viral infection in the regulation of pathogenic T helper cells in EAE.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; EAE; IL-17; Th17; ischemic brain injury.
Copyright © 2020 Milovanovic, Arsenijevic, Stojanovic, Kanjevac, Arsenijevic, Radosavljevic, Milovanovic and Arsenijevic.
Figures
References
-
- Rouvier E, Luciani MF, Mattéi MG, Denizot F, Golstein P. CTLA-8, cloned from an activated T cell, bearing AU-rich messenger RNA instability sequences, and homologous to a Herpesvirus Saimiri gene. J Immunol. (1993) 150:5445–56. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

