LITHOPHONE: Improving lncRNA Methylation Site Prediction Using an Ensemble Predictor
- PMID: 32582286
- PMCID: PMC7297269
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2020.00545
LITHOPHONE: Improving lncRNA Methylation Site Prediction Using an Ensemble Predictor
Abstract
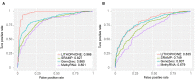
N 6-methyladenosine (m6A) is one of the most widely studied epigenetic modifications, which plays an important role in many biological processes, such as splicing, RNA localization, and degradation. Studies have shown that m6A on lncRNA has important functions, including regulating the expression and functions of lncRNA, regulating the synthesis of pre-mRNA, promoting the proliferation of cancer cells, and affecting cell differentiation and many others. Although a number of methods have been proposed to predict m6A RNA methylation sites, most of these methods aimed at general m6A sites prediction without noticing the uniqueness of the lncRNA methylation prediction problem. Since many lncRNAs do not have a polyA tail and cannot be captured in the polyA selection step of the most widely adopted RNA-seq library preparation protocol, lncRNA methylation sites cannot be effectively captured and are thus likely to be significantly underrepresented in existing experimental data affecting the accuracy of existing predictors. In this paper, we propose a new computational framework, LITHOPHONE, which stands for long noncoding RNA methylation sites prediction from sequence characteristics and genomic information with an ensemble predictor. We show that the methylation sites of lncRNA and mRNA have different patterns exhibited in the extracted features and should be differently handled when making predictions. Due to the used experiment protocols, the number of known lncRNA m6A sites is limited, and insufficient to train a reliable predictor; thus, the performance can be improved by combining both lncRNA and mRNA data using an ensemble predictor. We show that the newly developed LITHOPHONE approach achieved a reasonably good performance when tested on independent datasets (AUC: 0.966 and 0.835 under full transcript and mature mRNA modes, respectively), marking a substantial improvement compared with existing methods. Additionally, LITHOPHONE was applied to scan the entire human lncRNAome for all possible lncRNA m6A sites, and the results are freely accessible at: http://180.208.58.19/lith/.
Keywords: ensemble model; epitranscriptome; lncRNA; m6A; site prediction.
Copyright © 2020 Liu, Lei, Fang, Tang, Meng and Wei.
Figures
References
-
- Chen T., Guestrin C. (2016). XGBoost: A Scalable Tree Boosting System, in Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining (San Francisco).
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

