Identification of the cDNA Encoding the Growth Hormone Receptor (GHR) and the Regulation of GHR and IGF-I Gene Expression by Nutritional Status in Reeves' Turtle (Chinemys reevesii)
- PMID: 32582298
- PMCID: PMC7296147
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2020.00587
Identification of the cDNA Encoding the Growth Hormone Receptor (GHR) and the Regulation of GHR and IGF-I Gene Expression by Nutritional Status in Reeves' Turtle (Chinemys reevesii)
Abstract
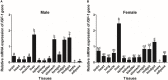
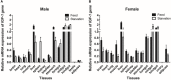
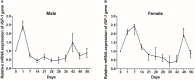
Chinemys reevesii (Reeves' turtle) is a slow-growing reptile that is distributed widely across China. Prior to this study, the cDNA sequence of the growth hormone receptor (GHR) in the Reeve's turtle, or how periods of starvation might influence the gene expression of GHR and insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) in this species, were unknown. Here, we identified the full-length sequence of the cDNA encoding GHR in Reeves' turtle by using RT-PCR and RACE. The full-length GHR cDNA was identified to be 3936 base-pairs in length, with a 1848 base-pair open reading frame (ORF) that encodes a 615 amino acid protein. Analysis showed that GHR mRNA was detectable in a wide range of tissues; the highest and lowest levels of expression were detected in the liver and the gonad, respectively. IGF-I was also expressed in a range of tissues, but not in the gonad; the highest levels of IGF-I expression were detected in the liver. After 4 weeks of fasting, the expression levels of GHR and IGF-I in the liver had decreased significantly; however, these gradually returned to normal after refeeding. We report the first cloned cDNA sequence for the GHR gene in the Reeve's turtle. Our findings provide a foundation from which to investigate the specific function of the GHR in Reeve's turtle, and serve as a reference for studying the effects of different nutrient levels on GHR expression in this species.
Keywords: Chinemys reevesii; GHR; IGF-I; Reeves’ turtle; starvation.
Copyright © 2020 Zhu, He, Ruan, Zhang, Liao, Gao, Lin, Chen, Liang and Liu.
Figures




References
-
- Belkin D. A. (1965). Reduction of Metabolic Rate in Response to Starvation in the Turtle Sternothaerus minor. Copeia 1965:367 10.2307/1440804 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

