Comparative analysis of transcriptomes revealed the molecular mechanism of development of Tricholoma matsutake at different stages of fruiting bodies
- PMID: 32582456
- PMCID: PMC7297875
- DOI: 10.1007/s10068-020-00732-8
Comparative analysis of transcriptomes revealed the molecular mechanism of development of Tricholoma matsutake at different stages of fruiting bodies
Abstract
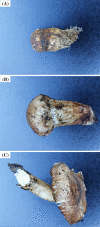
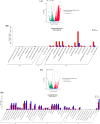
The purpose of the study is to investigate the molecular mechanisms of development of Tricholoma matsutake fruiting body at the primordial stage (TM-1), the intermediate stage (TM-2) and the mature stage (TM-3) using RNA-Seq sequencing technology. The analysis of gene expression level revealed that the Spn2 and Eef1a1 gene were the key genes in the primordial stage of T. matsutake by regulating cytokinesis, protein synthesis, and cell growth. And the Ubc, Atp6, Cytb, and Pth2 gene were the key genes in the mature stage of T. matsutake by regulating energy metabolism and protein synthesis. Differential expression genes (DEGs) analysis results showed that Cdc28, Rad53, Dun1, Pho85 and Pho81 were the key DEGs regulating cell cycle genes of T. matsutake from primordial stage to intermediate stage. And APC, Cyr1, Cdc45, Spo11 and Rec8 genes were the key DEGs for the meiosis and sporogenesis of T. matsutake from the intermediate stage to the mature stage.
Keywords: Development; Molecular mechanism; RNA-sequencing; Transcriptome; Tricholoma matsutake.
© The Korean Society of Food Science and Technology 2020.
Figures



References
-
- Addi C, Bai J, Echard A. Actin, microtubule, septin and ESCRT filament remodeling during late steps of cytokinesis. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2018;50:27–34. - PubMed
-
- Ando A, Harada A, Miura K, Tamai Y. A gene encoding a hydrophobin, fvh1, is specifically expressed after the induction of fruiting in the edible mushroom Flammulina velutipes. Curr. Genet. 2001;39:190–197. - PubMed
-
- Arima T, Yamamoto M, Hirata A, Kawano S, Kamada T. The eln3 gene involved in fruiting body morphogenesis of Coprinus cinereus encodes a putative membrane protein with a general glycosyltransferase domain. Fungal Genet. Biol. 2004;41:805–812. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
