Improvement of viscous substance production during Cheonggukjang fermentation added with glycine
- PMID: 32582457
- PMCID: PMC7297880
- DOI: 10.1007/s10068-020-00743-5
Improvement of viscous substance production during Cheonggukjang fermentation added with glycine
Abstract
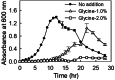
When Bacillus subtilis NB-NUC1 associated with Cheonggukjang fermentation was aerobically grown in a synthetic medium containing 1 to 2% glycine (w/v), cell growth was inhibited in a dose-dependent manner. Subsequently, different concentrations of glycine (0, 1, and 2%) were used in Cheonggukjang fermentation for 96 h at 40 °C. Supplementation of 1% glycine increased extracellular γ-glutamyl transpeptidase (γ-GTPase), responsible for the production of viscous substance. Based on correlation studies, we conclude that the production of viscous substance is correlated with viscous extension (r = 0.867), extracellular proteins contents (r = 0.821), and γ-GTPase activity (r = 0.807). The molecular weight of the viscous substance obtained during Cheonggukjang fermentation by B. subtilis NB-NUC1 was also affected by glycine supplementation. Our results demonstrate that glycine supplementation before solid-state fermentation may increase the mass production of mucilage in food industry.
Keywords: Bacillus spp.; Cheonggukjang; Glycine; Secretion; Viscous substance.
© The Korean Society of Food Science and Technology 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors have declared no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Best GR, Britz ML. Facilitated protoplasting in certain auxotrophic mutants of Corynebacterium glutamicum. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1986;23:288–293. doi: 10.1007/BF00261930. - DOI
-
- Han YW, Clarke MA. Production and characterization of microbial levan. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1990;38:393–396. doi: 10.1021/jf00092a011. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous