A New Design for the Fixed Primer Regions in an Oligonucleotide Library for SELEX Aptamer Screening
- PMID: 32582641
- PMCID: PMC7291870
- DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2020.00475
A New Design for the Fixed Primer Regions in an Oligonucleotide Library for SELEX Aptamer Screening
Abstract
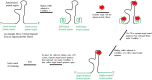
Single-stranded DNA or RNA oligonucleotides, often called aptamers, can bind to a molecular target with both high affinity and selectivity due to their distinct three-dimensional structures. A technique called systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment (SELEX) is used to screen aptamers from a random DNA or RNA pool, or library. The traditionally-designed oligonucleotides in libraries contain a randomized central region along with a fixed primer region at each end for amplifying target-bound central sequences. The single-stranded forward and reverse primer sequences may interfere with target-binding to the central region, resulting in a partial or complete loss of high-affinity aptamers during the SELEX process. To address this issue, researchers have modified the traditional oligonucleotide libraries and developed new types of oligonucleotide libraries; however, these approaches come with various limitations. The author proposes a new design that uses a conformation-changeable sequence as primers, which may open a new avenue for developing an optimized aptamer sequence with both high affinity for, and selective binding to, a particular target via SELEX.
Keywords: aptamer screening; fixed primer regions; i-motif; oligonucleotide library; systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment (SELEX).
Copyright © 2020 Wang.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources