Understanding Tick Biology and Its Implications in Anti-tick and Transmission Blocking Vaccines Against Tick-Borne Pathogens
- PMID: 32582785
- PMCID: PMC7297041
- DOI: 10.3389/fvets.2020.00319
Understanding Tick Biology and Its Implications in Anti-tick and Transmission Blocking Vaccines Against Tick-Borne Pathogens
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Understanding Tick Biology and Its Implications in Anti-tick and Transmission Blocking Vaccines Against Tick-Borne Pathogens.Front Vet Sci. 2020 Aug 31;7:575. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2020.00575. eCollection 2020. Front Vet Sci. 2020. PMID: 33062650 Free PMC article.
Abstract
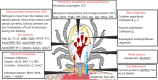
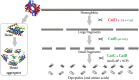
Ticks are obligate blood-feeding ectoparasites that transmit a wide variety of pathogens to animals and humans in many parts of the world. Currently, tick control methods primarily rely on the application of chemical acaricides, which results in the development of resistance among tick populations and environmental contamination. Therefore, an alternative tick control method, such as vaccines have been shown to be a feasible strategy that offers a sustainable, safe, effective, and environment-friendly solution. Nevertheless, novel control methods are hindered by a lack of understanding of tick biology, tick-pathogen-host interface, and identification of effective antigens in the development of vaccines. This review highlights the current knowledge and data on some of the tick-protective antigens that have been identified for the formulation of anti-tick vaccines along with the effects of these vaccines on the control of tick-borne diseases.
Keywords: Borrelia; Ixodes; anti-tick vaccines; blood; saliva; transmission-blocking.
Copyright © 2020 Bhowmick and Han.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

