Reirradiation for Recurrent Scalp Angiosarcoma: Dosimetric Advantage of PBT over VMAT and EBT
- PMID: 32582810
- PMCID: PMC7038915
- DOI: 10.14338/IJPT-19-00074
Reirradiation for Recurrent Scalp Angiosarcoma: Dosimetric Advantage of PBT over VMAT and EBT
Abstract
Purpose: Reirradiation in the scalp area can be challenging given the proximity to organs at risk (OARs), such as the eye and brain. Our aim is to evaluate the dosimetric differences of volumetric modulated arc therapy (VMAT) and electron beam therapy (EBT) compared with 3-dimensional proton beam therapy (PBT).
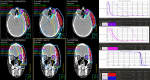
Patients and methods: We evaluated a patient with recurrent angiosarcoma of the left temporal scalp after prior surgical resections and radiation therapy to 60 Gy in 30 fractions who needed reirradiation. We generated VMAT, EBT, and PBT plans using the Pinnacle Treatment Planning System (TPS). Both VMAT and EBT plans used a skin bolus, whereas no bolus was used for the proton plan. Doses to the OARs, including cochlea, eyes, lens, lacrimal glands, optic nerves, optic chiasm, pituitary gland, and underlying brain, were compared.
Results: The reirradiation treatment dose was 60 Gy(RBE). Target volume coverage was comparable in all plans. Compared with VMAT and EBT, the PBT plan showed reductions in mean and maximum doses to all OARs. Without the use of protons, several OARs would have exceeded dose tolerance utilizing VMAT or electrons. Dose reduction of up to 100% was achieved for central and contralateral OARs.
Conclusion: Compared with VMAT and EBT, PBT resulted in dose reductions to all OARs, while maintaining excellent target coverage. PBT showed a significant advantage in treating superficially located skin cancers, such as angiosarcoma, without the need for a bolus. PBT can be considered in the upfront treatment and certainly in the reirradiation setting.
Keywords: Bragg peak; angiosarcoma; organ at risk prevention; periorbital tumors; proton beam therapy.
© Copyright 2019 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no relevant conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Proton Beam Therapy for Locally Advanced Head and Neck Tumors: An Analysis of Dosimetric and Clinical Outcomes.Am J Clin Oncol. 2022 Feb 1;45(2):81-87. doi: 10.1097/COC.0000000000000883. Am J Clin Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35073281
-
Volumetric-modulated arc therapy (VMAT) for whole brain radiotherapy: not only for hippocampal sparing, but also for reduction of dose to organs at risk.Med Dosim. 2017 Winter;42(4):375-383. doi: 10.1016/j.meddos.2017.07.005. Epub 2017 Aug 16. Med Dosim. 2017. PMID: 28822604
-
Proton Beam Therapy in the Treatment of Periorbital Malignancies.Int J Part Ther. 2021 Mar 26;7(4):42-51. doi: 10.14338/IJPT-20-00025.1. eCollection 2021 Spring. Int J Part Ther. 2021. PMID: 33829072 Free PMC article.
-
Proton versus Photon Radiotherapy for Pediatric Central Nervous System Malignancies: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Dosimetric Comparison Studies.J Oncol. 2019 Nov 27;2019:5879723. doi: 10.1155/2019/5879723. eCollection 2019. J Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31885580 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging Role of Carbon Ion Radiotherapy in Reirradiation of Recurrent Head and Neck Cancers: What Have We Achieved So Far?Front Oncol. 2022 May 23;12:888446. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.888446. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35677171 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Extramedullary Intradural Primary Spinal Angiosarcoma: A Case Study.Cureus. 2024 Nov 29;16(11):e74767. doi: 10.7759/cureus.74767. eCollection 2024 Nov. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 39734979 Free PMC article.
-
Cutaneous head and neck angiosarcoma: The 30-year UCLA experience.Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol. 2023 Oct 17;8(6):1557-1563. doi: 10.1002/lio2.1173. eCollection 2023 Dec. Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol. 2023. PMID: 38130244 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Goldblum JR, Folpe AL, Weiss SW, Enzinger FM. Enzinger and Weiss's Soft Tissue Tumors. Philadelpha, PA: Elsevier Inc; 2014.
-
- Oashi K, Namikawa K, Tsutsumida A, Takahashi A, Itami J, Igaki H, Inaba K, Yamazaki N. Surgery with curative intent is associated with prolonged survival in patients with cutaneous angiosarcoma of the scalp and face—a retrospective study of 38 untreated cases in the Japanese population. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2018;44(6):823–9. - PubMed
-
- Gragoudas ES, Lane AM, Regan S, Wenjun L, Judge HE, Munzenrider JE, Seddon JM, Egan KM. A randomized controlled trial of varying radiation doses in the treatment of choroidal melanoma. Arch Ophthalmol. 2000;118(6):773–8. - PubMed
-
- Egger E, Zografos L, Schalenbourg A, Beati D, Böhringer T, Chamot L, Goitein G. Eye retention after proton beam radiotherapy for uveal melanoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2003;55(4):867–880. - PubMed
-
- Tsina EK, Lane AM, Zacks DN, Munzenrider JE, Collier JM, Gragoudas ES. Treatment of metastatic tumors of the choroid with proton beam irradiation. Ophthalmology. 2005;112(2):337–43. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources