Monte Carlo Simulations of Neutron Ambient Dose Equivalent in a Novel Proton Therapy Facility Design
- PMID: 32582817
- PMCID: PMC7302728
- DOI: 10.14338/IJPT-19-00071.1
Monte Carlo Simulations of Neutron Ambient Dose Equivalent in a Novel Proton Therapy Facility Design
Abstract
Purpose: The neutron shielding properties of the concrete structures of a proposed proton therapy facility were evaluated with help of the Monte Carlo technique. The planned facility's design omits the typical maze-structured entrances to the treatment rooms to facilitate more efficient access and, instead, proposes the use of massive concrete/steel doors. Furthermore, straight conduits in the treatment room walls were used in the design of the facility, necessitating a detailed investigation of the neutron radiation outside the rooms to determine if the design can be applied without violating existing radiation protection regulations. This study was performed to investigate whether the operation of a proton therapy unit using such a facility design will be in compliance with radiation protection requirements.
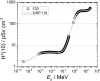
Methods: A detailed model of the planned proton therapy expansion project of the University of Texas, M. D. Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, Texas, was produced to simulate secondary neutron production from clinical proton beams using the MCNPX Monte Carlo radiation transport code. Neutron spectral fluences were collected at locations of interest and converted to ambient dose equivalents using an in-house code based on fluence to dose-conversion factors provided by the International Commission on Radiological Protection.
Results and conclusions: At all investigated locations of interest, the ambient dose equivalent values were below the occupational dose limits and the dose limits for individual members of the public. The impact of straight conduits was negligible because their location and orientation were such that no line of sight to the neutron sources (ie, the isocenter locations) was established. Finally, the treatment room doors were specially designed to provide spatial efficiency and, compared with traditional maze designs, showed that while it would be possible to achieve a lower neutron ambient dose equivalent with a maze, the increased spatial (and financial) requirements may offset this advantage.
Keywords: Monte Carlo study; neutron shielding; proton therapy.
©Copyright 2020 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: The authors have no relevant conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures


References
-
- Hall EJ, Kellerer AM, Friede H. Dependence on neutron energy of the OER and RBE. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1982;8:1567–72. - PubMed
-
- Hall EJ. RBE and OER values as a function of neutron energy. Eur J Cancer. 1974;10:297–9. - PubMed
-
- Lai BL, Sheu RJ, Lin UT. Shielding analysis of proton therapy accelerators: a demonstration using Monte Carlo-generated source terms and attenuation lengths. Health Phys. 2015;108:S84–93. - PubMed
-
- Sunil C. Analysis of the radiation shielding of the bunker of a 230MeV proton cyclotron therapy facility; comparison of analytical and Monte Carlo techniques. Appl Radiat Isot. 2016;110:205–11. - PubMed
-
- Titt U, Newhauser WD. Neutron shielding calculations in a proton therapy facility based on Monte Carlo simulations and analytical models: criterion for selecting the method of choice. Radiat Prot Dosimetry. 2005;115:144–8. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
