GABAergic interneurons excite neonatal hippocampus in vivo
- PMID: 32582852
- PMCID: PMC7292633
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.aba1430
GABAergic interneurons excite neonatal hippocampus in vivo
Abstract
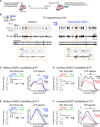
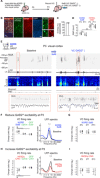
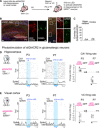
GABAergic interneurons are proposed to be critical for early activity and synapse formation by directly exciting, rather than inhibiting, neurons in developing hippocampus and neocortex. However, the role of GABAergic neurons in the generation of neonatal network activity has not been tested in vivo, and recent studies have challenged the excitatory nature of early GABA. By locally manipulating interneuron activity in unanesthetized neonatal mice, we show that GABAergic neurons are excitatory in CA1 hippocampus at postnatal day 3 (P3) and are responsible for most of the spontaneous firing of pyramidal cells at that age. Hippocampal interneurons become inhibitory by P7, whereas visual cortex interneurons are already inhibitory by P3 and remain so throughout development. These regional and age-specific differences are the result of a change in chloride reversal potential, because direct activation of light-gated anion channels in glutamatergic neurons drives CA1 firing at P3, but silences it at P7 in CA1, and at all ages in visual cortex. This study in the intact brain reveals that GABAergic interneuron excitation is essential for network activity in neonatal hippocampus and confirms that visual cortical interneurons are inhibitory throughout early postnatal development.
Copyright © 2020 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works. Distributed under a Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License 4.0 (CC BY-NC).
Figures

References
-
- Le Magueresse C., Monyer H., GABAergic interneurons shape the functional maturation of the cortex. Neuron 77, 388–405 (2013). - PubMed
-
- Duan Z. R. S., Che A., Chu P., Modol L., Bollmann Y., Babij R., Fetcho R. N., Otsuka T., Fuccillo M. V., Liston C., Pisapia D. J., Cossart R., De Marco García N. V., GABAergic restriction of network dynamics regulates interneuron survival in the developing cortex. Neuron 105, 75–92.e5 (2020). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Marques-Smith A., Lyngholm D., Kaufmann A.-K., Stacey J. A., Hoerder-Suabedissen A., Becker E. B. E., Wilson M. C., Molnár Z., Butt S. J. B., A transient translaminar gabaergic interneuron circuit connects thalamocortical recipient layers in neonatal somatosensory cortex. Neuron 89, 536–549 (2016). - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

