Downregulation of microRNA‑143 promotes osteogenic differentiation of human adipose‑derived mesenchymal stem cells through the k‑Ras/MEK/ERK signaling pathway
- PMID: 32582994
- PMCID: PMC7388841
- DOI: 10.3892/ijmm.2020.4651
Downregulation of microRNA‑143 promotes osteogenic differentiation of human adipose‑derived mesenchymal stem cells through the k‑Ras/MEK/ERK signaling pathway
Abstract
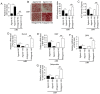
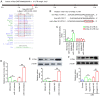
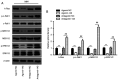
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are known to have regulatory roles in the osteogenic differentiation of various mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), although their regulatory role on human adipose‑derived mesenchymal stem cells (hADSCs) remains unclear. The aim of the present study was to investigate the biological function and underlying molecular mechanism of miRNAs in regulating the osteogenic differentiation of hADSCs using microarray assay. hADSCs differentiated into osteoblasts under culture with osteogenic medium, with an increase observed in calcium deposits and alkaline phosphatase activity. The mRNA levels of bone sialoprotein, osteopontin and osteocalcin increased, whereas Runt‑related transcription factor‑2 expression decreased during osteogenic differentiation. In addition, miR‑143 was markedly downregulated during osteogenic differentiation, while miR‑143 overexpression inhibited and miR‑143 knockdown enhanced this process. miR‑143 overexpression also blocked extracellular signal‑regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2) pathway activation, while miR‑143 inhibition enhanced it. The promoting effects of miR‑143 knockdown on the osteogenic differentiation of hADSCs were partly diminished by the mitogen‑activated protein kinase (MEK) inhibitors U0126 and PD98059. Bioinformatics analysis further revealed that miR‑143 targets k‑Ras and directly binds to the 3'‑untranslated region of its mRNA. Inhibition of miR‑143 enhanced the activation of the k‑Ras/MEK/ERK pathway during osteogenic differentiation, whereas miR‑143 overexpression had the opposite effect. Collectively, these results demonstrated that miR‑143 negatively regulates the osteogenic differentiation of hADSCs through the k‑Ras/MEK/ERK pathway, providing further insight into the underlying molecular mechanisms.
Figures




References
-
- Alvira-González J, Sánchez-Garcés MÀ, Cairó JR, Del Pozo MR, Sánchez CM, Gay-Escoda C. Assessment of bone regeneration using adipose-derived stem cells in critical-size alveolar ridge defects: An experimental study in a dog model. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2016;31:196–203. doi: 10.11607/jomi.4190. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Sánchez-Garcés MÀ, Alvira-González J, Sánchez CM, Barbany Cairó JR, Del Pozo MR, Gay-Escoda C. Bone regeneration using adipose-derived stem cells with fibronectin in dehiscence-type defects associated with dental implants: An experimental study in a dog model. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2017;32:e97–e106. doi: 10.11607/jomi.5169. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

